Revised Good Manufacturing Practices


Revised Good Manufacturing Practices
Current Affairs
La Excellence IAS Academy | October 7, 2023
CONTEXT: The government recently directed all pharmaceutical companies in the country to implement the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), bringing their processes to par with global standards.
WHAT ARE GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICES (GMP)?
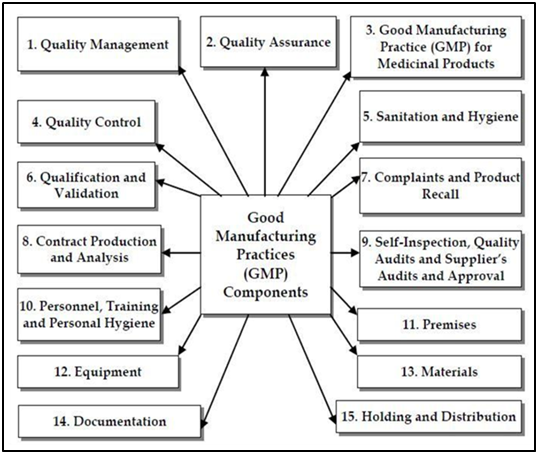
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is a set of guidelines and standards established by regulatory agencies to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products, as well as other products like food, medical devices, and cosmetics.
Key principles and components of Good Manufacturing Practices include:
NEED FOR IMPROVED STANDARDS:
- Global Alignment: The adoption of new norms bridges the gap between India’s pharmaceutical practices and international standards, fostering global harmonization and promoting cross-border confidence in Indian-manufactured medicines.
- Contamination Concerns: A series of instances involving alleged contamination in India-manufactured medicines in various countries has raised serious concerns. These incidents, such as the deaths linked to products in Gambia, Uzbekistan, the United States, and Cameroon, emphasize the importance of stringent quality control measures.
- Deficiencies in Manufacturing Units: Government inspections of manufacturing units revealed critical deficiencies in processes, infrastructure, and personnel qualifications. The absence of quality failure investigations, inadequate testing of raw materials, and subpar documentation further underscored the need for comprehensive reforms.
- Limited Compliance: A majority of India’s drug manufacturing units do not meet global standards, with only a fraction being WHO-GMP certified. The revised standards seek to rectify this disparity and enhance overall compliance.
- Low Compliant: Presently, only 2,000 of 10,500 manufacturing units in the country were found to be compliant with WHO-GMP standards.
KEY CHANGES IN REVISED GMP GUIDELINES:
- Pharmaceutical Quality System: The guidelines establish a comprehensive pharmaceutical quality system, integrating quality risk management, product quality reviews, and equipment validation. This system mandates regular quality assessments, consistency verification, and preventive measures against defects.
- Stability Studies: Companies must conduct stability studies under varying climatic conditions to ascertain product quality over time. This includes maintaining drugs in stability chambers with controlled temperature and humidity, and conducting accelerated stability tests.
- Enhanced Documentation: The new guidelines emphasize thorough documentation of processes, which is critical for gaining global regulatory approval. Proper documentation ensures transparency, traceability, and adherence to prescribed procedures.
- IT-Backed Quality Control: The guidelines stipulate the implementation of GMP-related computerized systems to prevent data tampering, unauthorized access, and omission of critical data. These systems enhance data accuracy, facilitate audits, and prevent manipulation.
- Expanded Scope: The revised GMP guidelines include requirements for various product types, including biological products, agents with radioactive ingredients, and plant-derived products. The guidelines also cover manufacturing of investigational products for clinical trials.
IMPLICATIONS AND BENEFITS:
- Short-Term Impacts:
- Temporary Disruption: Initially, as pharmaceutical companies adapt to the new GMP guidelines, there might be disruptions in production, distribution, and supply chains. This could temporarily affect the availability of some medicines for export markets.
- Transition Costs: Companies, especially smaller ones, may need to invest in infrastructure, technology, and training to align with the new standards. This could lead to increased operational costs, affecting profit margins in the short term.
- Export Delays: The time required to implement the new standards might cause delays in meeting export demands. Regulatory approvals from importing countries may also require additional scrutiny during this transition period.
- Long-Term Impacts:
- Enhanced Credibility: As Indian pharmaceutical companies align with global GMP standards, the reputation of the “Made in India” label is likely to improve. This enhanced credibility could boost the trust of international regulators and consumers in Indian-manufactured medicines.
- Increased Access to Markets: Many countries require adherence to stringent GMP standards for pharmaceutical imports. By conforming to these standards, Indian pharmaceutical companies can gain access to a wider range of markets that demand high-quality products.
- Reduced Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with international GMP standards could result in fewer regulatory barriers and inspections by foreign authorities. This could facilitate smoother exports and reduce the risk of export bans or recalls due to quality concerns.
- Competitive Advantage: India’s reputation as a reliable source of generic medicines could be further solidified by the implementation of improved GMP practices. This could give Indian pharmaceutical companies a competitive advantage in global markets.
- Diversification of Products: The revised GMP guidelines encourage the manufacturing of a broader range of products, including biological and plant-derived products. This diversification could enable Indian companies to tap into new markets and expand their export portfolios.
- Higher Export Volumes: As trust in the quality of Indian pharmaceuticals grows, there’s potential for an increase in export volumes. This, in turn, could contribute to economic growth and job creation within the pharmaceutical sector.
CHALLENGES TO CONSIDER:
- Costs and Affordability: The transition to new GMP standards could lead to increased costs, which might be passed on to consumers. Balancing quality improvements with affordability remains a challenge.
- Smaller Enterprises: Smaller pharmaceutical companies might face greater difficulties in implementing the new standards within the stipulated time frame. This could potentially impact their ability to compete in international markets.
- Global Competition: Other countries with established GMP practices might still maintain an advantage in terms of regulatory relationships and market presence. India will need to effectively communicate its commitment to quality improvements to gain a competitive edge.
CONCLUSION:
India’s endeavor to implement the revised Good Manufacturing Practices demonstrates its commitment to producing high-quality pharmaceuticals and fostering a reputable pharmaceutical industry on the global stage. By addressing contamination concerns, deficiencies in manufacturing units, and compliance disparities, the country aims to solidify its position as a reliable and quality-centric provider of generic medicines. This step not only ensures the well-being of its citizens but also strengthens its role as a significant player in the international pharmaceutical landscape.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
