Landslides


Landslides
Current Affairs Daily News & Issues
La Excellence IAS Academy | October 7, 2023
Why in News: Recent Landslide incident in Himachal Pradesh
WHAT ARE THE REASONS FOR LANDSLIDES?
|
Natural Factors |
Anthropogenic Factors |
| · Earthquake- Shocks and Vibrations
· Heavy rainfall and snowfall leads to loosening of the soil layers. |
· Unplanned construction activities near the slopes
· Building dams near the weak zones · Deforestation · Overgrazing |
WHAT ARE THE IMPACTS OF LANDSLIDES?
- Lead to economic decline: Landslides results in destruction of property. If the landslide is significant, it could drain the economy of the region or country.
- Destruction of infrastructure: Infrastructure such as roads, railways, leisure destinations, buildings and communication systems gets affected by landslide.
- Loss of life: Communities living at the foot of hills and mountains are at a greater risk of death by landslides.
- Impacts river ecosystems: The soil, debris, and rock sliding downhill can find way into rivers and block their natural flow. It may cause flood. Many river habitats like fish can die due to interference of natural flow of water. Communities depending on the river water for household activities and irrigation will suffer if flow of water is blocked.
Vulnerability of Himalayan Ecosystem to Landslide:
- The Himalayan ecosystem, being young and rugged, is fragile due to tectonic and neo-tectonic activities.
- Subsurface processes (rock deformation, erosion) and surface processes (weathering, precipitation) contribute to fragility.
- Climatic impacts like freezing/thawing, heavy rain/snow, cause landslides, avalanches, debris flow, and flash floods.
- Anthropogenic activities and climate change worsen vulnerability.
- Glaciers, rivers, geomorphology, biodiversity are affected, compounded by land degradation.
- Slope gradient, elevation, rock strength, forest cover, urbanization, sediment type contribute to landslide susceptibility.
- Deforestation, river flow, and debris flow weaken slopes, enhancing landslide risk.
Needed Steps:
- Monitoring and Early Warning Systems:
- Establishing resilience involves a sensor network, real-time monitoring, data analysis, and AI/ML-based Early Warning Systems (EWS).
- Tools like rain gauges, piezometers, inclinometers, InSAR, total stations aid monitoring in landslide-prone areas.
- Himalayan States Council for Disaster Management:
- Creation of a Council of Himalayan States to assess surface/subsurface stresses, simulate hazard scenarios, and coordinate disaster management.
- Collaboration among states crucial for knowledge and resource sharing in disaster preparedness.
- Balancing Development and Sustainability:
- Region’s resources (glaciers, minerals, energy, tourism) support sustainable socioeconomic growth.
- Need for balance between resource use and ecological preservation.
- Town planning must consider the mountain’s specifics, drainage, slope management, retaining walls, and building codes.
- High-resolution Mapping and Building Codes:
- Essential to map towns in high resolution, assess load-bearing capacity, and frame effective building codes.
- Measures include limiting heavy constructions, ensuring proper drainage, scientific slope management for disaster resilience.
NDMA GUIDELINES FOR LANDSLIDE DISASTER MANAGEMENT
NDMA follows a 9 –step process to manage Landslides. These include the following major elements to enhance the effectiveness of managing landslide hazard in the country:
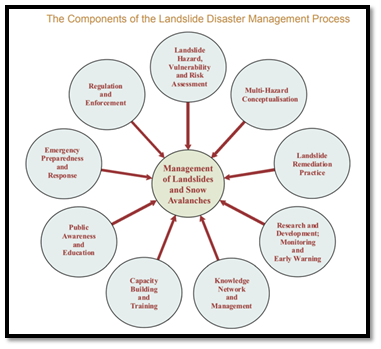
NDMA GUIDELINES ON LAND SLIDE MITIGATION
|
DRR-Structural measures |
DRR-Non structural measures |
Capacity development |
| Protection of
Human settlements |
Site selection for Human
Settlements in Landslide and Snow Avalanche Prone Areas |
Training |
| Protection of heritage Structures | Regulations and building codes | Curriculum Development |
| Multi-Hazard shelters | Licensing and certification
Of professionals |
Community- Based Disaster Management |
| Surface Drainage Control Works | Public Private Partnerships | Mock Drills/Exercises |
| Building retaining walls; increasing Vegetation cover | Insurance | Vocational Training / Skill Development |
| Regulation of Land Use Practices for development activities | Use of Drone Technology for regular monitoring | Empowering Women, marginalised communities , persons with disabilities |
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
