

Deep Fakes: We should aim to curb the Liar’s Dividend(Mint)
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology (T)
Topic: Emerging Technologies
Issue: Deepfakes
Synopsis:
- A deepfake is an artificial image or video generated by a special kind of machine learning called “deep” learning.
Issues:
- Liars Dividend : Anyone who is caught on tape doing something wrong will be able to dismiss the evidence of wrongdoing by claiming it is just another deep fake.
- Evidence can be so easily falsified that nothing can be relied upon to serve as legitimate evidence of wrongdoing.
- Misinformation and Fake News
- Political Manipulation
- Erosion of trust in media and information sources
Source: The Hindu
IMF says global ‘soft landing’ in sight, lifts 2024 growth outlook.
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy
Topic: Indices and reports
Issue: World Economic Outlook
Context: Latest “World Economic Outlook” report released by IMF.
Synopsis:
- The combination of steady growth and falling inflation has raised hopes for a so-called soft landing for the global economy (soft landing is a slowdown sufficient to contain inflation without causing a recession).
- Raised India’s growth projection to 6.7% in FY24 due to “resilient domestic demand”.
| International Monetary Fund(IMF)
● Is an international financial institution established in 1944. ● Objectives: To promote international monetary cooperation, exchange rate stability, balanced trade growth, and financial stability. ● Reports by IMF ○ World Economic Outlook ○ Global Financial Stability Report Fiscal Monitor |
Source: The Hindu
India nominates 12 forts of Marathas for UNESCO World Heritage List.
Syllabus: GS-I
Subject: History-Art and Culture
Topic: Art and architecture
Issue: World Heritage Sites
Context: India has nominated the “Maratha Military Landscapes” for inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage list for 2024-25.
Maratha Military Landscapes:
- These are a network of forts that showcase the strategic military powers of Maratha rule.(Examples – Khanderi, Raigad, Rajgad, Pratapgad forts)
- Developed between the 17th and 19th centuries.
| UNESCO World Heritage Sites:
● Designated for their cultural, historical, scientific or other forms of significance. ● Process for selection: Nominated by the host country and determined by the international committee to be a unique landmark. ● Objective: Conservation, protection from human or animal trespassing, unrestricted access, or threat from local administrative negligence. At present in India, there are 42 World Heritage sites out of which 34 are cultural sites, 7 are natural sites and 1 is a mixed site. |
Source: The Hindu
Centre starts survey to assess women participation in workforce.
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Society and Social Justice (S)
Topic: Welfare schemes, mechanisms, laws and institutions related to Women.
Issue: Female Labour Force Participation Rate
Context: The Union Ministries of Labour & Employment and Women & Child Development have started a joint survey on increasing women participation in the workforce.
Synopsis:
- As per Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) the women participation in labour force was.
(Data for Mains)
- Labour codes – specific provisions for safeguarding the employment of women workers:
- The Code on Social Security, 2020 provides for
- enhanced paid maternity leave,
- provision for mandatory crèche facilities in establishments having 50 or more employees,
- permitting women workers in the night shifts with adequate safety measures, etc.
- The Code on Occupational Safety, Health And Working Conditions, 2020 has proposed tweaks in employment terms and conditions for women workers in the above-ground mines.
- The Code on Wages 2019 has provisions for no gender-based discrimination for wages in an establishment for similar nature of work i.e. equal pay for equal work.
- The Code on Social Security, 2020 provides for
Source: The Hindu
Astronomers spot unusual object falling in the black hole ‘mass gap’.
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Space Technology
Issue: Astronomy Concepts
Synopsis:
- The mass determines a star’s life cycle.
- Neutron Stars: When stars run out of fuel, their cores collapse under their own gravity.
- If the core is less dense, it becomes a neutron star, else it becomes a black hole.
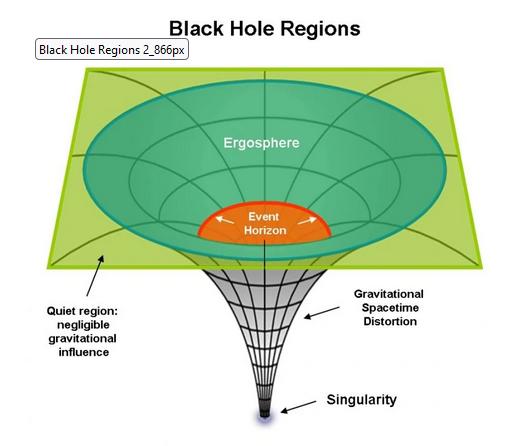
- Event Horizon:It is the point of no-return where the gravitational pull becomes so immense that not even light can escape.
-
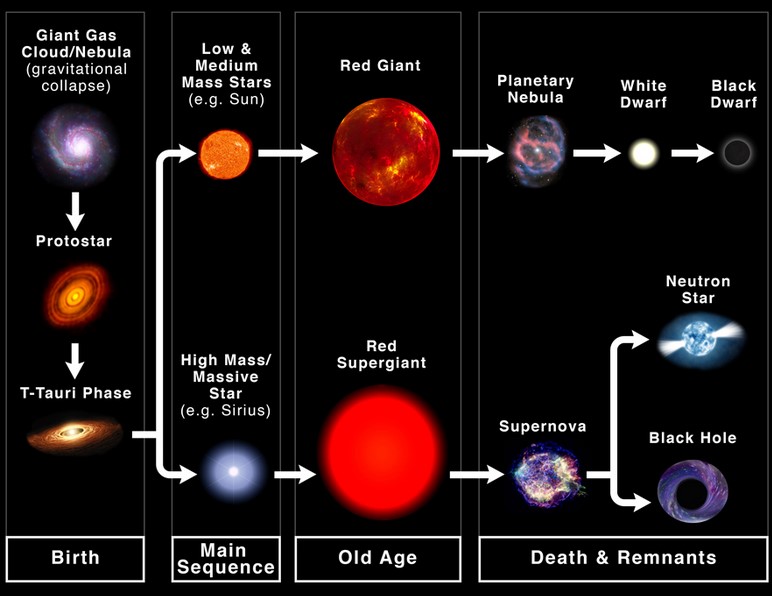
- Singularity is the heart of the black hole, a point of infinite density where all the matter that fell in is concentrated.
- Chandrasekhar limit:Only stars whose mass is greater than 44 times of the sun turns into neutron stars/blackholes.
- Black Hole mass gap: Mass gap between heaviest possible neutron stars, (2.2 solar masses) and the lightest black holes(5 solar masses).

- Pulsars:Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars with strong magnetic fields that blast out pulses of radiation at regular intervals ranging from seconds to milliseconds.
- Millisecond Pulsars: Rotate significantly faster, with periods less than about 10 milliseconds.
- Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity : It suggests that instead of thinking of gravity as a force between masses, it is the bending or warping of space and time.
- Space and time are not separate entities but are interconnected called ad “spacetime”.
- Massive objects, like planets and stars, warp or curve the fabric of spacetime around them.
- Predicted the existence of gravitational waves – ripples in spacetime caused by the acceleration of massive objects.
Source: The Hindu
AMU minority status | Institute of national importance must reflect national structure: Govt. to SC
Syllabus: GS-II;
Subject: Society and Social Justice
Topic: Welfare schemes, mechanisms, laws, and institutions related to minorities.
Issue: Inclusion of AMU to the list of Institutions of National Importance.
Context: Ongoing Supreme Court dispute over Aligarh Muslim University’s minority status and reservation implications raises complex constitutional questions.
Government’s Position:
- Institutions recognized as institutions of national importance, such as AMU, must reflect the national structure.
- Declaring AMU as a minority institution would imply no reservation for SC, ST, and SEBC categories, raising concerns about social justice and equality.
Petitions and Arguments:
- Petitions challenging AMU’s minority status were filed in the 93rd amendment.
- Despite no reservation, approximately 70-80% of students in AMU are Muslims.
- SC erred in assuming Muslims were a minority in 1920 when AMU was established.
- Article 30 rights cannot be extended retroactively without determining minority status at the time of establishment.
Conclusion:
Overall, the case raises important questions about the intersection of minority rights, educational institutions’ status, and constitutional provisions regarding reservation and social justice.
Article/Judgement in News (Mains)
| Article 30 :
The right of religious and linguistic minorities to establish and administer educational institutions. Article 15: The 93rd Amendment Act of 2005: clause 5 was added to Article 15, which enables the reservation for socially and economically backward classes in private educational institutes. 1967 five-judge SC Constitution bench :‘S Azeez Basha vs Union of India’: It was held that AMU was not entitled to minority education status as it “was neither established nor administered by the Muslim minority” |
“Institute of National Importance” (INI): They are premier higher educational institutions recognized by the Central Government through an act of Parliament. . They receive special funding and recognition from the Government of India, along with the authority to grant degrees as per Section 22 of the University Grants Commission Act, 1956. While the specific criteria for achieving INI status and the associated benefits are not explicitly outlined, these institutions enjoy elevated status and support for their educational endeavors. |
Source: Indian Express
First-ever survey puts India’s snow leopard count at 718.
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Environment
Topic: Species in News.
Issue: A survey report on Snow Leopard.
Context: According to a first-of-its-kind, four-year-long estimation exercise, India has an estimated 718 snow leopards in the wild.
Key points highlighted by the survey:
- India is home to an estimated 10% of the global Snow Leopard population.
- The highest number of snow leopards were found in Ladakh, followed by Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and Jammu and Kashmir.
- It is a collaborative effort involving various organizations including the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), the World Wide Fund for Nature-India, and the Nature Conservation Foundation, Mysuru.
- Faces threats from factors such as human-wildlife conflict, poaching, and habitat loss.
| (Prelims) Species in news: Snow leopard
· IUCN Status: ‘vulnerable’. · Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Schedule I. · CITES: the Appendix Iand Appendix I Convention on Migratory Species (CMS). · It is a large cat native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia- including the Himalayas, and Russia’s remote Altai mountains. · Snow leopard range countries formed the Global Snow Leopard Forum (GSLF) and signed the Bishkek Declaration. · Indian National Parks where the Snow Leopard is likely to be spotted: o Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary – Himachal Pradesh o Ulley Valley – Ladakh o Hemis National Park – Himachal Pradesh Project Snow Leopard : · Launched in 2009, by the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate. · To promote an inclusive, participatory, and landscape-based approach to conserving Snow Leopards and their habitat in India. · The project is operational in five Himalayan states: Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
|
Source: The Hindu
US begins re-imposing sanctions on Venezuela, oil may come next
Syllabus: GS- II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: Agreements Affecting India’s interests
Issue: Sanctions on Venezuela
Implications of US sanctions:
- May reduce international trade with that particular country, by denying investment, foreign exchange or credit to the target country.
India’s oil imports from Venezuela:
- India is the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil and depends on imports to meet over 85 percent of its requirements.
- Venezuela has the largest proven oil reserves in the world.
- Venezuela was India’s fifth largest oil supplier in 2019, but imports stopped after US sanctions.
- Hence re-imposition of sanctions doesn’t largely affect India.
Source: Indian Express
