China to develop Sri Lanka deep sea port and airport.
| Syllabus: GS-II; Subject: International Relations; Topic: India and its neighborhood, Issue: China –Sri Lanka Relations. |
Context: China has pledged to develop Sri Lanka’s strategic deep-sea port and airport.
Key Highlights:
- China, being Sri Lanka’s biggest bilateral creditor, will assist in restructuring Sri Lanka’s external debt.
- China has offered to assist in developing Colombo International Airport and Hambantota port.
- The Hambantota port was leased to a Chinese state-owned company in 2017 for 99 years.
Prelims Connect (Places in news)
| Hambantota port:
· It is located right in middle of vital energy supply lines in Indian Ocean, connecting Middle East and East Asia. · Situated on the southern coast of Sri Lanka. · Constructed as part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
|
Source: The Hindu
New MGNREGA rates: Goa sees highest hike of Rs 34 per day, UP, Uttarakhand lowest at Rs 7
| Syllabus: GS-II; Subject: Current affairs, Topic: Schemes/Policies/Programmes, Issue: MGNREGA |
Context: Announcement of revised MGNREGA wage rates by The Ministry of Rural Development.
Synopsis:
- Objective: Ensure fair compensation for unskilled manual labourers participating in MGNREGA projects.
- State Variations: Highest Hike: Goa, Lowest Hike: Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- Wage rates are determined based on changes in CPI-AL, reflecting rural inflation.
Prelims Connect (Schemes/Policies)
| MGNREGA:
· Offers 100 days of work annually to rural adults for unskilled manual labor. · Focuses on building durable assets like wells, ponds, roads, and canals in rural areas. · At least one-third of beneficiaries must be women, promoting gender equality. · Work should be provided within 15 days of demand; otherwise, an unemployment allowance is given. · Mandatory regular social audits ensure transparency and accountability in the scheme’s implementation. Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Labourers (CPI-AL): ü Measures changes in the cost of living for agricultural labourers. ü Compiled by the Labour Bureau. ü Used to fix minimum wages for labourers. ü Helps policymakers make informed decisions. |
Source: Indian Express
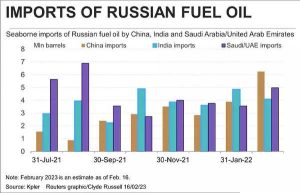
Sanctions unlikely to majorly hit Russian oil flows to India.
| Syllabus: GS-II Subject: International Relations Topic: Global issues, Issue: India’s oil imports from Russia. |
Context: Latest round of US sanctions targeting Russian shipping major Sovcomflot.
Likely Outcomes:
- Muted impact expected on overall trade.
- Possibility of deeper discounts on Russian oil.
- Shift of crude deliveries to China noted.
- Minimal impact due to vast opaque tanker fleet.
- India remains the top importer despite sanctions.
  |
Source: Indian Express
India achieves 16% decline in new TB cases and, 18% reduction in mortality since 2015: Report.
| Syllabus: GS-III; Subject: Science & Technology; Topic: Medical science and Health, Issue: Tuberculosis Cases |
Context: The findings of the report on Tuberculosis and Lung Cancer.
Highlights:
- India has achieved a 16% decline in new TB cases since 2015.
- Uttar Pradesh sees a significant increase in TB notifications.
- National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP) continues free diagnostic services.
- NTEP is a public health initiative launched by the Government of India to organize and manage the country’s efforts against tuberculosis (TB).
Lung Cancer:
- WHO recognizes lung cancer as a significant public health concern.
- Primarily linked to smoking tobacco.
Prelims Connect (Diseases in News)
| Tuberculosis
ü A contagious bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. ü Primarily affects the lungs but can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. Types: ü Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Affects the lungs. includes primary TB pneumonia and miliary TB. ü Extra pulmonary Tuberculosis: Seen in immunocompromised patients. Symptoms of Tuberculosis: Coughing up blood and mucus. |
Source: The Hindu
Daily Editorials
India Pakistan question of trade
| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India and its neighborhood, Issue: India-Pakistan |
Context: Pakistan’s Foreign Minister said his country may “seriously examine” the question of resuming trade with India.
Reasons for reconsideration-
- Economic pressures and potential logistical efficiency drive the resumption of trade.
- Pakistan’s declining relative power and regional tensions with Afghanistan, Iran.
Challenges
- Lack of consensus within Pakistan
- India insists on addressing terrorism before advancing trade talks.
- Domestic politics in both countries complicate the path to improved economic ties.
The way ahead
- Resuming bilateral trade could benefit both economies, particularly in sectors like agriculture.
- Private diplomacy may pave the way for future negotiations.
Source: Indian Express
State of employment in India: what a new report say about youth and women concern and caution
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Unemployment and issues, Issue: Measuring unemployment & Indices, trends, reports |
Context: India Employment Report 2024 released by the Institute for Human Development and International Labor Organization
Key findings of the report:
- Women’s labor force participation rate (LFPR’0 in 2022 was 32.8%, which is 2.3 times lower than men’s LFPR of 77.2%.
- Almost 82% of the workforce engaged in the informal sector.
- Self-employment is the primary source of employment, accounting for 55.8% in 2022.
- The share of agriculture in total employment fell to around 42% in 2019 from 60% in 2000, with construction and services absorbing this shift.
The way ahead:
- Promote job creation and improve employment quality.
- Address labour market inequalities and strengthen skills development.
- Bridge knowledge deficits on labour market patterns and youth employment.
- Address challenges in gig or platform work, such as job security and irregular wages.
- Boost productive non-farm employment, particularly in manufacturing.
- Provide support to micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises, including digitalization and AI tools and a cluster-based approach to manufacturing.
Source: Indian Express
Experiment with water
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Pollution, Issue: Water Pollution |
Drinking water issue:
- Only 10% of Indian cities meet drinking water standards.
- Water quality degrades in distribution networks due to old pipes, sediment buildup, and pathogen accumulation.
- The demand for packaged drinking water (PDW) is rising as a result.
The way ahead:
- Reconsidering treating large quantities for drinking when only a fraction is used.
- Segregating water for drinking and other domestic uses
- Decentralized treatment and non-pipe delivery.
- Bengaluru and Delhi are experimenting with water ATMs to address water crises.
- More experiments and technological advancements are needed.
Source: Indian Express
Why are Rohingya refugee risk their lives at sea
| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Global issues, Issue: Rohingya refugee |
Context: A boat carrying Rohingya refugees overturned off the coast of Indonesia.
Rohingyas:
- A Muslim minority ethnic group originating from the Arakan Kingdom in Myanmar.
- Myanmar has denied them citizenship since 1982.
- Their exodus began in 2017 following violence in Rakhine state.
- The UN has described the 2017 violence as ethnic cleansing and accused the Myanmar government of genocidal intent.
- Currently nearly 9.60 lakh Rohingya refugee lives in Bangladesh.
Reasons for undertaking hazardous sea routes:
- Overcrowding and inadequate access to healthcare and education.
- Gang violence and arson attacks
Conclusion:
- Indian Ocean countries must address this issue regionally.
Source: The Hindu
On sustainable building materials
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Indian Initiatives, efforts, and Commitments, Issue: Energy Efficient Building |
Need for energy efficient building:
- The building sector consumes over 33% of India’s electricity.
- India Cooling Action Plan foresees an eight-fold increase in cooling demand by 2037.
- To address escalating energy and cooling demand, heat islands, climate change.
Existing initiatives:
- Eco-Niwas Samhita (ENS) and Residential Energy Conservation Building Code.
Concerns
- Priority to fast-paced, energy-intensive techniques over climate-appropriate design.
- Knowledge about climate-appropriate design and architecture is lacking.
- High initial costs hinder the adoption of climate-responsive building practices.
The way ahead:
- Innovation from manufacturers to develop cost-effective, durable, and climate-resilient solutions.
- Reimagining construction practices and fostering sustainability culture are essential.
| Prelims Connect (Schemes/Policies):
The Eco-Niwas Samhita (ENS) is a two-part code developed by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) in India to promote energy-efficient residential buildings. Components: ENS 2018 (Part I: Building Envelope): Focuses on the building’s shell, including walls, roof, and windows. ENS 2021 (Part II: Electro-Mechanical and Renewable Energy Systems): This part addresses the building’s mechanical and electrical systems, including lighting, air conditioning, and renewable energy sources. |
Source: The Hindu
WTO’s investment facilitation negotiations are not illegal
| Syllabus: GS II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Regional and global groupings, Issue: World Trade Organization (WTO) |
Context: Non-adoption of the agreement on investment facilitation for development (IFD) at MC13 of the WTO
Investment facilitation for development (IFD):
- Negotiations for an IFD agreement began in 2017 on a plurilateral basis by 70 countries.
- The agreement was finalized in November 2023.
- The agreement aims to create legally binding provisions to facilitate investment flows.
- Focuses on enhancing regulatory transparency and administrative procedures to boost foreign investment.
- Lacks provisions on market access, investment protection, and investor-state dispute settlement (ISDS).
India’s concern with IFD:
- India highlights the absence of a mandate for WTO negotiations on investment.
- India refers decisions from the 2004 General Council and 2015 Nairobi ministerial.
- IFD negotiations were launched on a plurilateral basis, not multilateral, challenging the application of the negative mandate.
Conclusion:
- Plurilateral agreements like the IFD agreement are viewed as essential for revitalizing the WTO’s legislative function amidst consensus challenges.
- India, as a major economy, may benefit from reevaluating its defensive stance on issues like the proposed IFD Agreement.
| Prelims Connect (Plurilateral agreements)
· Article II.3 of the WTO Agreement permits plurilateral agreements, which bind accepting member countries without obligating non-participants. · PAs offer a mechanism for advancing specific trade objectives among willing WTO members. |
Source: The Hindu
Preventing a China-Taiwan conflict
| Syllabus: GS- II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Global issues, Issue: China-Taiwan conflict |
India’s stance and interests:
- Trade with Taiwan has increased seven-fold since 2001, ongoing discussion for FTA.
- Growing importance of Taiwan in the semiconductor industry -partnership between Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation and the Tata Group.
- Aggression against Taiwan would disrupt global trade, affecting critical supply chains.
- A conflict over Taiwan could escalate tensions along the India-China border.
The way ahead:
- Leverage international law and constructing narratives to discourage Chinese aggression towards Taiwan.
- Proactive engagement mitigates risks posed by Chinese aggression and aligns with India’s self-interest.
Source: The Hindu