WTO unveils new rule for simplifying services trade, India stays out.
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Trade and External sector, Issue: WTO MC 13
Context: The 13th Ministerial Conference (MCA 13) of the World Trade Organization announced new rules to streamline the international trade in services.
Highlights:
- Aim: To simplify procedures, make authorization processes more transparent and accessible.
- promote equal opportunities for service suppliers world wide.
- India is not a party to the agreement.
- Dialogue on Plastic Pollution: To reduce plastics pollution and promote environmentally sustainable trade in plastics.
Fact: India is the fifth-highest generator of plastic waste in the world.
| WTO’s Ministerial Conference:
● It is the highest decision-making body of the WTO ● The 13th Ministerial Conference is underway in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. |
Source: Mint
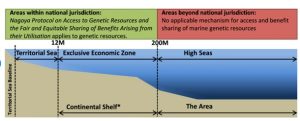
Current approaches for addressing overfishing flawed: India at the WTO.
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Trade and External sector, Issue: Fisheries Subsidies
Context: WTO negotiation session on fisheries subsidies in the Abu Dhabi Ministerial Conference-13.
Fisheries Subsidies:
- India urged for a moratorium on subsidies for fishing beyond the exclusive economic zone (EEZs).
- Current approaches for addressing “Over Capacity and Over Fishing” (OCOF) are deeply flawed.
- Any agreement on fisheries subsidies should be built on the principle of Common But Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR- RC).
- Sovereign rights of members for sustainable management of fisheries within their Exclusive Economic Zones should be protected.
Agreement on Fisheries Subsidies – Geneva Package MC 12 : Prohibited harmful fisheries subsidies that contribute to overfishing and depletion of fish stocks.
| United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS):
An international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities.
|
Source: Indian Express
Air no longer ‘poor’: Curbs to tackle pollution withdrawn in Delhi
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Pollution, Issue: Air Pollution
Context: withdrawal of all measures to control pollution in Delhi-NCR, on the account of improvement in air quality.
Air Quality Index (AQI):
- It is a measure of air quality. The higher the AQI, the worse the air.
- There are six categories of AQI, namely ‘Good’ (0-50), ‘Satisfactory’ (50-100), ‘Moderately polluted’ (100-200), ‘Poor’ (200-300), ‘Very Poor’ (300-400), and ‘Severe’ (400-500).
- The pollutants measured include PM 10, PM 2.5, NO2, SO2, CO, O3, NH3, and Pb.
Graded Response Action Plan or GRAP:
- It is a set of emergency measures used to prevent deterioration of air quality in the Delhi-NCR region.
- Implemented by the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
Prelims Connect : (Institutions in News)
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- It is a statutory body.
- Established under Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region and Adjoining Areas Act, 2021
- Responsible for forming air pollution reduction strategies for the region and overseeing their implementation.
- Replaced the Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA).
Source: Indian Express
CAA rules likely to be notified before poll code, to seek proof of India entry, religion
Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Citizenship, Issue: Citizenship Amendment Act, 2019
Why in News: notifying the rules for implementation of the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA), 2019.
Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA), 2019
- amended the Citizenship Act, 1955.
- Objective: To provide Indian citizenship for persecuted religious minorities from three specific neighbouring countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.
- It allows migrants from these three countries to apply for Indian citizenship through the naturalisation
Criticisms:
- Violates Article 14 (equality): For discriminating based on religion.
- Difficult to differentiate between illegal migrants and those persecuted.
- Other refugees, that include Tamils from Sri Lanka not covered under the Act.
| Prelims Connect: (Terms in News)
· Citizenship is a subject matter under the Union list and hence only Parliament can make laws regarding it. · Naturalization is the legal process by which a non-citizen acquires the nationality of a country after birth. |
Source: Indian Express
‘10,000 genome’ project completed, says Centre
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Science and Technology, Topic: Bio technology, Issue: Genome India Project
Context: The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) announced the completion of the ‘10,000 genome’ project.
Genome Sequencing:
- the process of determining the complete order of the chemical building blocks, called bases, that make up an organism’s DNA.
- The bases are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanines, and Thymine.
The Genome India Project:
- Aim: To collect 10,000 genetic samples from citizens across India.
- to build a reference database of whole genome sequences.
- Led by Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru and Centre For Cellular And Molecular Biology (CCMB), Hyderabad.
- Benefits:
- gain deeper insight into India’s population diversity,
- find genetic predispositions to disease,
- develop personalised and customisable drugs,
- improve gene therapy etc.
Human Genome Project:
international research effort to determine the sequence of the human genome and identify the genes that it contains.
Source: The Hindu
BJP gains in U.P., Himachal RS polls amid cross-voting
Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Legislature, Issue: Rajya Sabha Elections
Context: Elections to 15 Rajya Sabha seats conducted by Election Commission.
Elections to Rajya Sabha:
- Composition: Maximum strength is fixed at 250.
- 238 are elected indirectly and 12 are nominated by the president.
- The Fourth Schedule of the Constitution: allocation of seats in the Rajya Sabha to the states and union territories.
- Term: 6 years as provided in the Representation of the People Act (1951)
- elections to one-third seats are held every two years.
- Procedure: Elected by the elected MLAs of the State in accordance with the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote.
- Open ballot system – an MLA has to show the ballot paper to a nominated agent of that political party.
Can a whip be issued for Rajya Sabha election?
- A whip cannot be issued for voting in the Rajya Sabha elections as the election is not a business of the house.
- However, cross-voting can be interpreted by the speaker as “voluntarily giving up the membership of a party” and disqualification proceedings can be initiated under Xth schedule.
Prelims Connect (Terms in News):
- A whip is a written order that party members be present for an important vote, or that they vote only in a particular way.
- Proportional representation: an electoral system in which the distribution of seats corresponds closely with the proportion of the total votes cast for each party.
Source: The Hindu
Daily Editorials
Why culture was recognized as a goal for the first time under India’s G20 presidency
Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Global groupings, Issue: G-20
Importance of culture in global co-operation:
- plays a pivotal role in achieving all 17 SDGs.
- It has transformative impact on society.
- the potential to ensure a more equitable, just, and sustainable world for generations to come.
Alignment with India’s foreign policy:
- Reflects India’s rich heritage and commitment to holistic sustainability.
- India leverages its cultural heritage to develop innovative solutions, promoting sustainable choices and embracing a circular economy.
- Embracing culture as a core component of the global development agenda is essential for a brighter, more harmonious future for all nations and peoples.
India’s tariff regime: Costs of a barrier
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Trade and external sector, Issue: India’s trade policy
Tariff regime of India:
- India steadily reduced tariffs from the early 1990s until 2014.
- Increase in tariff is driven by the call for self-reliance.
- India’s tariffs are now higher than China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh, affecting export competitiveness and hurting consumers.
Conclusion:
- A more balanced approach to protectionism.
- Reduction in duties on components to attract manufacturers.
- Alongside tariff reduction, India must pursue trade agreements with countries like the UK and the EU to boost exports and promote manufacturing.
Source: Indian Express
Burden of power: On India’s astronauts and the Indian space policy
Syllabus: GS- III, Subject: Science and technology, Topic: Space Technology, Issue: Gaganyaan-Human space flight mission
Context: Prime Minister released the name of shortlisted candidate for Gaganyaan Mission
Significance:
- Gaganyaan aligns with Indian Space Policy 2023.
- Emphasizes maintaining India’s edge in human spaceflight and developing sustained presence in space.
The way ahead:
- Future missions must justify objectives transparently for public scrutiny.
- Emphasis should be on democratic space exploration over geopolitical aims.
- Space exploration should prioritize scientific and societal value over “space superpower” status.
Source: The Hindu
Decoding consumption: On the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Growth, Development and inclusion, Issue: Household Consumption Expenditure Survey
Context: Household Consumption Expenditure Survey released by Statistics Ministry
- Conducted by NSSO every five years.
- Average monthly per capita consumer expenditure rose more than 30% in cities and more than 40% in rural areas since 2011-12.
- Proportion of monthly spends on food has slipped below 50% in rural homes (to 46.4%), and under 40% in urban homes.
Key concerns:
- The average spending increase in rural and urban areas over the last 11 years falls considerably below inflation and GDP growth rates.
- Despite significant transfers under welfare schemes,
- Decrease in monthly spend towards food suggest a possible decrease in Consumer inflation.
- The finding of survey becomes more important due to absence of census data.
Source: The Hindu
Why sustainable funding matters for India’s ‘science power’ ambition.
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Science and Technology, Topic: Policy and Mission, Issue: India’s Research & Development (R&D) spending
Spending on R&D:
- India’s R&D expense has decreased.
Issues:
- Insufficient and primarily dependent on public funds.
- Private sector is resistant due to.
- Poor capacity to evaluate R&D in India.
- ambiguous regulatory roadmaps.
- lack of clear exit options for investors in sectors, and
- fears of intellectual property rights theft.
- Underutilization of government budget.
Suggestions:
- Increase contributions from the private sector
- Mitigating under-spending and under-utilization of R&D funds.
- Incentives for private investment like tax rebates and clear regulatory roadmaps.
- Bureaucratic capacity to evaluate and monitor science projects.
Conclusion:
Sustainable funding for science is crucial for India’s journey towards sustainable development.
| +1 Advantage for Mains (data points)
India’s R&D expense: the current 0.64% of GDP, 0.8% in 2008-2009 and 0.7% in 2017-2018. Ø Science, Technology, and Innovation Policy (2013) – Increasing Gross Expenditure on R&D (GERD) to 2% GDP as a national goal. Ø Much below than Average spending of developed countries on R&D ( between 2% and 4% of GDP). Ø To reach developed nation status India needs to spend at least 3% of the GDP on R&D annually until 2047. Data on percentage of spending by various sector Ø In 2020-2021, private sector industry contributed 36.4% of the GERD whereas the Union government’s share was 43.7%. |
Source: The Hindu
The current global order — a fraying around many edges
Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Global issues, Issue: Issues in Global Order
Global Order: aimed at upholding sovereign equality and collective security among nations
- Post-World War order initiated with
- Declaration of the United Nations in 1942
- endorsement of the Atlantic Charter in 1941.
- International economic order created by: Bretton Woods Conference (1944) through the establishment of
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- World Bank (WB)
- General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), later succeeded by World Trade Organization (WTO) in 1994.
- Key issue with the global order:
- Bias: The WB and IMF governance structures favor the United States and Europe reflecting old power structures.
- UN system, based on international treaties, favors original signatories.
- Efforts to challenge the biased global order–
- the Non-Aligned Movement and
- G-77,
- ad hoc groups like OECD, QUAD
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank etc.
The emergence of regional, ad hoc organizations indicates a need for reform in the global order.
| +1 Advantage for Mains
Examples of dominance in global order: · An American citizen always heads the World Bank; · ‘Europe’ (Western Europe, in practice) gets to nominate the head of the IMF. IMF voting right favor America and Europe: · Voting right of original BRICS members (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) are 2.22, 2.59, 2.63, 6.08 and 0.63. · Voting right US and European countries The U.S 16.5, U.K. (4.03), Germany (5.31) and the rest of the G-7 percentage approaches 30. · By this USA can effectively reject any reform. |
Source: The Hindu