

Sensing China threat, India joins race to mine sea patch.
| Syllabus: GS-I; Subject: Geography; Topic: Resources – World and India. Issue: India to mine sea patch. |
Context: India seeks exploration rights from International Seabed Authority.
Key Highlights:
- Targets Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (AN Seamount) rich in minerals.
- Also applied for Carlsberg Ridge exploration.
Issues:
- Reported Chinese activity in the region.
- Sri Lanka claims rights to AN Seamount under separate laws.
- Exploration rights specific to open ocean areas.
- Continental Shelf Commission may impact India’s plans.
Prelims Connect (Institutions in News):
| International Seabed Authority (ISA):
· Headquarters: Kingston, Jamaica. · Established in 1994 to regulate mining in the international seabed beyond national jurisdiction. · Created upon the entry into force of the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). · Organizes and controls mineral resources activities in the Area for the benefit of humankind. · Ensures effective protection of the marine environment from harmful effects of deep-seabed activities. · Functions: Grants licenses and regulates exploration and exploitation of mineral resources in the international seabed. |
Source: The Hindu
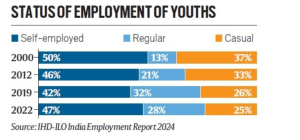
India’s employment conditions continue to be poor: Report
| Syllabus: GS-III; Subject: Economy, Topic: Indices and Reports, Issue: Employment Conditions, ‘India Employment Report 2024’ |
Context: the findings of the ‘India Employment Report 2024’.Top of Form
India Employment Report 2024: it released by the Institute for Human Development (IHD) and International Labour Organisation (ILO).
Findings:
- Slow non-farm transition.
- Youth unemployment.
- Emphasizes the industry’s role in hiring.
- Challenges in skill initiatives persist.
- Unemployment among educated youth, especially women, is a concern.
Suggestions:
- Focus on boosting non-farm employment.
- More support for small enterprises and urban policies.
- Skills development and active labor market policies require enhancement.
- Key policy areas include job creation, employment quality, and bridging inequalities.
Prelims Connect (Institutions in News):

The International Labour Organization: it is a United Nations agency.
- The main aims of the ILO are to promote rights at work, encourage decent employment opportunities, enhance social protection and strengthen dialogue on work-related issues.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Founded: 1919.
- The Institute for Human Development (IHD) is a non-profit autonomous institution.

Source: Indian Express
80% of CPCB green funds unused: NGT told
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Indian Initiatives, Issue: Green Funds. |
Context: Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) spending of green funds.
- It has only used 20% of Environment Protection Charge (EPC), and Environmental Compensation (EC).
| Environmental Protection Charge (EPC):
· It is a fee imposed by the Supreme Court of India on new diesel vehicles with an engine capacity of 2000 cc and above that are registered in Delhi-NCR. · This fee is collected to combat pollution and is directed to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). Environmental Charge(EC): · It is a fee imposed to cover costs associated with environmental schemes related to the sale of electricity. · It’s typically a fixed percentage of all invoice charges, excluding certain other charges and taxes |
Prelims Connect (Institutions in News)
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB):
- It is a statutory organization under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- It was established in 1974 under the Water Act, 1974.
- The CPCB is also entrusted with the powers and functions under the Air Act, 1981.
- It monitors air and water quality.
Source: Indian Express
Bar on political activities as bail conditions is rights violation, says SC.
| Syllabus: GS-II; Subject: Polity; Topic: Rights Issues, Issue: Bail Conditions. |
Context: Supreme Court quashes bail condition restricting political activities.
Observations:
- The Supreme Court nullified the ban on political activities as a bail condition.
- The court said such condition is a breach of fundamental rights.
+ Prelims Connect:
| Bail Conditions In India:
ü Bail is the release of an accused person from custody with the promise to appear in court for trial. ü Governed by the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), bail can be statutory, regular, or anticipatory. ü Bail conditions may include surrendering passports or attending court hearings. ü Eligibility for bail depends on factors like the nature of the crime, past criminal record, and evidence strength.
|
Source: Indian Express
Daily Editorials
Footing the climate action bill
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Global agreements and efforts, Issue: UNFCCC |
Context: COP29, in Baku, Azerbaijan, is going to set NCQG New Collective Quantitative Goal (on finance).
New Collective Quantitative Goal(NCQG)
- It aims to mobilize more finance for climate action in developing countries.
- Current climate finance falls short of the promised $100 billion annually.
- Trillions are needed yearly for climate action, with more required by 2050.
- UN Climate Change faces financial issues despite advocating for more finance.
- The new amount must be transparently monitored and used for various climate needs.
Source: Indian Express
ICCC: Integrated farm data dashboard for customised solutions
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Agriculture and allied, Issue: Agriculture extension services |
Context: Recently Agriculture Minister inaugurated the Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) in New Delhi.
Krishi ICCC
- Tech-based solution within the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare.
- Utilizes AI, remote sensing, and GIS for agricultural data processing.
- Aims for comprehensive farm sector monitoring via geospatial integration.
- Generates farmer-specific advisories by correlating various data sources.
- Applications include custom advisories, drought actions, and crop analysis.
- K-DSS (Krishi Decision Support System) acts as a data repository for evidence-based decision-making.
How Delhi Talks to world
| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India’s Foreign Policy, Issue: Including foreign policy in electoral manifesto. |
Context: Foreign policy discussions need to be included in electoral manifesto.
Importance of including foreign policy in electoral dialogue
- Attention to foreign policy in election manifestos could bridge the gap between India’s global rise and domestic discourse.
- The Indian political class must articulate concrete foreign policy goals instead of prioritizing abstract claims of autonomy.
- The government aims to make India a developed nation by 2047, requires debate on economic strategy and global challenges.
- India’s low per capita income underscores the developmental challenges despite its growing economy.
- The Opposition plays a crucial role in debating policy issues and shaping foreign policy discourse.
Source: Indian Express
The need to curb black carbon emissions
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Pollution, Issue: Black carbon |
Context: Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) addressing the concern of black carbon
Black carbon:
- Emitted during incomplete combustion of biomass and fossil fuels.
- Exposure leads to heart disease, birth complications, and premature death.
- PMUY has reduced black carbon emissions by promoting the use of cleaner fuels.
Concerns:
- 25% PMUY of beneficiaries still cook solely with traditional biomass.
- Availability issues and last-mile connectivity gaps hinder PMUY’s success.
- Reliance on traditional fuel disproportionately affect women and children.
Recent steps to address this concern:
- Prime Minister announced a further ₹100 price reduction in March 2024,
- The government plans to continuously increase the spending since the scheme’s inception.
The way ahead:
- Panchayats can take the initiative to produce coal-bed methane gas from biomass.
- Prioritizing black carbon reduction is crucial for India’s global leadership in SDG.
| +1 Advantage For Mains (Data Point)
· In 2022-2023, 25% of PMUY beneficiaries, approximately 2.69 crore people, used either zero or just one LPG refill. · An August 2023 report by The Hindu found that the average PMUY beneficiary household consumes only 3.5-4 LPG cylinders annually, compared to 6-7 cylinders used by regular non-PMUY households. · According to a 2016 study, the residential sector contributes 47% of India’s total black carbon emissions, with industries contributing 22%, diesel vehicles 17%, open burning 12%, and other sources 2%. |
Source: The Hindu
The democratic political process is broken
| Syllabus: GS II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Elections and RPA, Issue: Election Process |
Political process
- Democratic politics aims to foster constructive collaboration and consensus building.
- Public discourse is essential for the exchange of ideas and opinions necessary to reach consensus.
Impediments affecting public discourse:
- Institutional news media’s loss of credibility.
- Content creation on social media prioritizes virality over substance.
- Media proliferation fragments collective attention.
- Civil society increasingly relies on the state for legitimacy, shifting away from its role as an independent voice.
- Political parties prioritize internal affairs over policy discussion, limiting constructive dialogue.
- Uncertain electoral benefits deter representatives from influencing policy agendas, favoring direct interventions for constituent services.
Conclusion:
- These interconnected issues resist easy solutions, but efforts must be made to address them in the world’s largest democracy.
Source: The Hindu
A cry for help, a call for reflection and action
| Syllabus: GS- I, Subject: Society and Social Justice, Topic: Social sector – Health, Issue: Mental health |
Context: Increasing incidents of depression and suicide among young students,
Factors responsible:
- Job scarcity and high fees fuel fierce competition in education.
- Parental expectations often disregard a child’s interests.
- Financial constraints limit access to educational resources.
- Changing family dynamics weaken family bonds, affecting social connections.
- Educational institutions often lack emotional support for students.
- Socioeconomically disadvantaged communities face discrimination, worsening their challenges.
| +1 Advantage For Mains (Data Points)
· Government administers only ~21% of colleges, while ~78% are under private entities (AISHE report, 2019-20). · Asia accounted for nearly 61% of global suicide fatalities in 2008 (The Lancet). · In 2022, over 13,000 Indian students committed suicide, comprising 7.6% of total suicide fatalities (NCRB report). · More than half of India’s population, 53.7%, consists of individuals under 25 years old. |
Source: The Hindu
