

Govt., conducting a feasibility study on integrating e-NAM with ONDC
Syllabus: GS-III;
Subject: Economic Development;
Issue: Integration of e_NAM with ONDC.
- Integration aims to benefit buyers, and sellers, and bolster resilience against market disruptions.
- It could empower farmer-producer organizations (FPOs) to trade seamlessly across platforms.
- Key contributors: mobility, food, and grocery, with expansion into fashion, and electronics.
- Efforts to on-board SMEs, and rural sellers for inclusive economic participation.
Conclusion:
- Integration signifies a pivotal step in streamlining agricultural trade and advancing India’s digital economy.
| Take Away Notes (Prelims)
e-NAM (Electronic National Agriculture Market): · Online trading platform linking Agricultural Produce Market Committees (APMC) mandi nationwide. · Aims to establish a unified market for agricultural commodities, facilitating electronic sales for farmers. · Participating states provide e-NAM software free of cost. ONDC (Open Network for Digital Commerce): · A government initiative in India aimed at creating a unified digital commerce platform. · It promotes openness, interoperability, and data security while empowering MSMEs. Its goal is to revolutionize digital commerce, fostering innovation and inclusive growth. |
Source: The Hindu
3Five judge SC Bench to sit today to hear conflict between Calcutta High Court judges.
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Judiciary and Tribunals
Topic: Jurisdiction of SC and HC – Spatial and Functional
Issue: Review Jurisdiction.
Hierarchy of judicial orders:
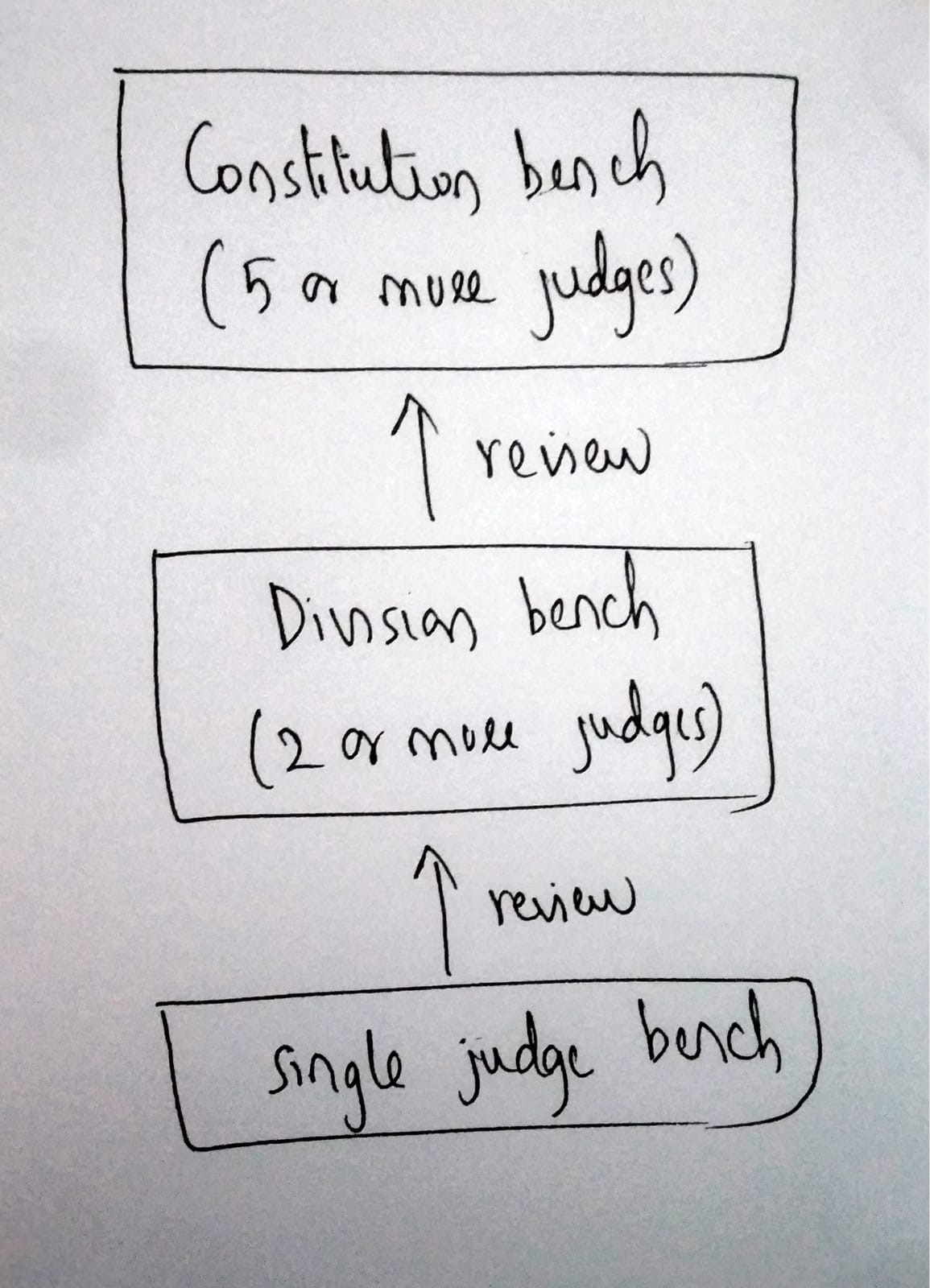
Review jurisdiction:
- The Supreme Court has the power to review its own judgements/orders by virtue of Article 137 of the constitution.
- Every High court, being the court of record under Article 215 also has the power to review their own judgements.
- The judgements of larger benches are legally binding on smaller benches. Small benches cannot either doubt/disobey the orders of larger benches.
Appellate jurisdiction:
- The judgements of subordinate courts can be appealed in High Courts and the judgements of High courts in Supreme Court.
- Under Article 141, the law declared by the Supreme Court shall be binding on all courts within the territory of India.
Source: The Hindu
Israel must take measures to prevent genocidal acts in Gaza and permit aid: ICJ.
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations (I)
Topic: International institutions, agencies and fora
Issue: Israel-Palestine
Synopsis:
- South Africa approached ICJ after the indiscriminate attacks on Gaza by Israel alleging a violation of Genocide Convention of 1948.
- ICJ said that Israel must prevent genocidal acts in Gaza and facilitate “urgently needed” humanitarian aid into Gaza.
The Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide (Genocide Convention), signed in 1948, is an international treaty that criminalizes genocide and obligates state parties to pursue the enforcement of its prohibition.
The Convention defined genocide as any of five “acts committed with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial or religious group”.
| International Court of Justice:
● Established in 1945, ICJ is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations (UN) ● HQ: The Hague, Netherlands ● Composition: 15 judges elected for nine-year terms by the UN General Assembly and the Security Council. ● Functions: ○ Settles legal disputes between states ○ Gives advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorised UN organs and specialised agencies. ● The decisions of the court are legally binding. ● Enforcement: Although legally binding, the court has no mechanism to enforce its decisions and hence sometimes the rulings goes completely ignored ○ Example: The court has ordered Russia to stop its invasion of Ukraine which clearly was ignored. |
Source: The Hindu
India-France defence ties take a bigger leap
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: India’s relations with major powers
Issue: India-France relationship
- A “defence industrial roadmap”
- for cooperation on defence production and
- for future collaboration on “co-design and co-development” of military hardware.
- Identified domains of collaboration range from aircraft to land and maritime warfare, especially underwater domain awareness, to space, robotic technology, cyber-defence, and artificial intelligence-led vehicles.
- Other agreements:
- Defence-space partnership that will help collaborate on “space situational awareness” and
- An MoU on coordinating satellite launches.
- Defence deals in the pipeline
- The 26 Rafale-M fighter jets for the Indian Navy’s aircraft carriers
- Three additional Scorpene-class conventional submarines.
Issues:
- Press visa restrictions-French government raised the issue of a French journalist who could be deported.
- No breakthrough on the civil nuclear cooperation agreement to build reactors at Jaitapur that was first signed in 2009.
Source: The Hindu
