

Governor R N Ravi’s walkout deepens Tamil Nadu crisis: Time to abolish governorships?
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Polity
Topic: Executive
Issue: Governor’s role in state
Role of governor as per constitution:
- Governor is required by the Constitution to act only in accordance with the aid and advice of the council of ministers and as such,
- Governor act as a bridge between the elected governments at the state and the Union.
Supreme Court’s observation in A G Perarivalan vs State (2022) case
- Governor is a “short-hand expression for state government”
- Governor has no discretionary power in matters of governance.
On financial devolution among States
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Polity
Topic: Federalism ,
Issue: Financial relation
Southern state have raised issue of not receiving proper share in financial devolution:
- Divisible pool of taxes are defined in article 270 of constitution divided as per recommendation of Finance Commission(Article 280)

Key issues
- Around 23% of Union government’s gross tax receipts are collected through Cess and surcharge, not shared with states.
- Variations exist in the amount each state receives back for every rupee contributed to central taxes. (Due to headquarter of corporations in few State capitals.)
- Higher weightage for equity and needs over efficiency.
- Grants-in-aid recommended by FCs vary among states, is based on population and area.
The way ahead:
- Enlarge the divisible pool by including a portion of Cess and surcharge, while gradually discontinuing various impositions to rationalize tax slabs.
- Increase weightage for efficiency criteria in horizontal devolution,
- Considering relative GST contributions from states.
- a more formal arrangement for states’ participation in the constitution and working of the Finance Commission, akin to the GST council.
- States should devolve adequate resources to local bodies for vibrant and accountable development, furthering the balance between equity and federalism.
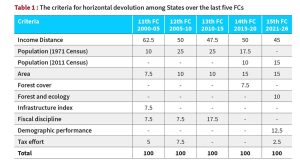
| Prelims connect( meaning of different term used in Finance Commission formula)
· Income distance’ is the distance of a State’s income from the State with highest per capita income which is Haryana. · ‘Population’ is the population as per the 2011 Census.(from 15th FC) · ‘Forest and ecology’ consider the share of dense forest of each State in the aggregate dense forest of all the States. · ‘The demographic performance’ criterion has been introduced to reward efforts made by States in controlling their population. · ‘Tax effort’ as a criterion has been used to reward States with higher tax collection efficiency. |
Electoral season and restructuring the health system
Syllabus: GS-I
Subject: Society and Social Justice
Topic: Social Sector-Health
Issue: Approach to public health in India
Approach to public health in India:
- Two main political parties in India treat health either as public good as citizen’s right or a commodity provided through public private partnership.
- Both approach find reflection in – National Rural Health Mission, National Medical Commission, Strengthened rural health infrastructure with capital investment, Social health insurance , National Health Authority , expansion of medical college
- Key concerns– Week primary and secondary health infrastructure, shortage of human resource
What India should do to reform its health system?
- Strengthening primary health: care is crucial for integrating community surveillance, demographic data, and disease profiles.
- Mapping and accrediting health facilities: expand access points and increase accountability through service packages.
- Coordination and capacity building: at the local level to regulate patient flows and ensure continuity of care.
- Successful examples like Thailand’s Universal Health Coverage emphasize planned strategies and strong HR policies.
- Establishing IT and monitoring systems linked to financing improves efficiency and outcomes within a decentralized, accountable framework.
Collapse of the ecological balance and an undeclared war with nature
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Ecology and Environment
Topic: Biodiversity and Conservation
Issue: Human Animal Conflict
Reason behind increase in human animal conflict:
- Forestlands cleared for non-forest use initiate ecosystem destruction,
- Such destruction get worsened by Monoculture plantations and pesticide use leading to soil depletion, reduced crop yields, and diseases.
- Expansion of resorts and tourism, especially in forest edges and elephant corridors
- Cattle grazing, planting invasive plants, and forest fires contribute to destruction of habitat.
The way ahead:
- Government efforts must focus on continuous conservation, public awareness, and stakeholder engagement.
- A high-level panel and Rapid Response Teams to address immediate issues.
- A statutory body is necessary to coordinate forest issues across departments to assess the situation and develop effective strategies.
- Strict enforcement of the Forest Conservation Act with Free and Prior Informed Consent (FPIC) principle is essential.
| +1 Advantage for mains ( data point)
· A study report titled Right of Passage: Elephant Corridors of India conducted by Wildlife Trust of India identified 88 elephant corridors in 2005. · As per the report, 24% of the corridors were under reserve forest and 76% under forest, agriculture, tea gardens, and human settlements. · In Kerala alone there were 20,957 cases of crop loss due to incursions by wild animals, leading to the death of 1,559 domestic animals, primarily cattle. (Between-2017-23) |
Beyond shelter, dweller needs within the four walls
Syllabus: GS- I
Subject: Society and social justice
Topic: Poverty, hunger and development related issues
Issue: Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin (PMAY-G)
- In the interim budget (2024) announcement was made for construction of two crore additional house in next five years and new housing scheme for middle class.
- Rapid housing sector expansion prompts consideration of trade-offs between quality of life and environmental concerns.
- Affordable housing often prioritizes speed, cost, and ease of construction over factors like thermal comfort and low-carbon infrastructure.
- Light House Projects (LHPs) under PMAY utilize modern technologies to build resilient and affordable houses.
- Technologies like Mivan offer efficiency but may contribute to increased heat gain and reliance on cooling appliances, elevating GHG emissions.
- Integration of passive design strategies is crucial for ensuring thermal comfort and aligning housing initiatives with environmental goals.
- Implementation of guidelines like Eco Niwas Samhita can facilitate a thermally comfortable environment within built spaces.
- The Smart Ghar III project in Rajkot, serves as a model for achieving indoor thermal comfort through passive design implementation
- An ecosystem change is needed to incentivize developers and raise awareness among stakeholders for passive design adoption.
- Weaving environmental consciousness into housing initiatives ensures resilience to climate change and contributes to a sustainable future.
| Prelims Connect
· Global Housing Technology Challenge – India (GHTC-India) to identify and mainstream a basket of innovative construction technologies from across the globe for housing construction sector that are sustainable, eco-friendly and disaster-resilient (Initiated by MoHUA ) · Light House Projects (LHPs) are underway as part of the Global Housing Technology Challenge (GHTC), spanning six sites across six States. · LHPs leverage modern technology and innovative processes to reduce construction time and build more resilient and affordable houses for the underprivileged. +1 Advantage (data point) · PMAY scheme has facilitated the construction of nearly three crore rural and 80 lakh urban affordable houses since 2015. |
Ending discrimination: On the Union of India and Others vs Ex. Lt. Selina John case
Syllabus: GS-I
Subject: Society and social justice
Topic: Issue of women
Issue: Discrimination at workplace
Recently in Union of India and Others, vs Ex. Lt. Selina John case Supreme Court declared discharge of a women employee after marriage as unconstitutional.
- Other discrimination faced by women:
- Barriers in education, employment, and opportunities
- Uncomfortable personal questions during job interview (about marriage and motherhood)
- Many girls drop out of school due to economic constraints and lack of facilities
- Government schemes for girls and women may not be effective if they are constrained by restrictive social and cultural norms.
- UN’s Gender Snapshot 2023: Without corrective measures, the next generation of women will continue to face disproportionate burdens of household duties and lack access to leadership roles .
| +1 Advantage (Data Point)
· Labour participation of women in the workforce in the latest Periodic Labour Force data (October-December 2023), is at an abysmal 19.9% for women of all ages. Observation of Supreme Court in the current case) “Terminating employment because the woman has got married is a coarse case of gender discrimination and inequality. Acceptance of such [a] patriarchal rule undermines human dignity, right to non-discrimination and fair treatment.” |
New treatments are emerging for type-1 diabetes
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Medical science and Health,
Issue: Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes:
| Islets of Langerhans are tiny clusters of specialised cells nestled within the pancreas.
They play a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels by producing hormones like insulin and glucagon. The islets are composed of beta cells that produce insulin. Insulin helps cells absorb glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream, lowering blood sugar levels. |
- Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Emerging treatments are trying to replace beta cells in the body by transplantation from human donors.
Differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
| Feature | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
| Cause | Autoimmune attack on insulin-producing cells | Insulin deficiency or body’s resistance to insulin |
| Onset | Usually rapid, often in childhood | Gradual, usually in adults |
| Symptoms | More pronounced: increased thirst, urination, weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision | May be mild or absent: increased thirst, urination, fatigue |
| Treatment | Requires lifelong insulin | Varies: lifestyle changes, medications, insulin (sometimes) |
Source: Mint
Let’s proceed with IMEC despite Gaza war, says Greek PM.
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: India’s relations with other nations
Issue: India-Greece
Context: State Visit of Prime Minister of Greece Mr. Kyriakos Mitsotakis to India.
Synopsis:
- Mitsotakis inaugurated the annual Raisina Dialogue.
- Despite the Israeli war in Gaza destabilising plans for the India-Middle East Economic Corridor (IMEC), India and Greece should persevere with the “peace project”, said the Greek PM.
- Greece had decided to join the Indo-Pacific Oceans initiative.
+1 Advantage (Statements for Mains):
- “To India, Greece is the natural doorstep to Europe and beyond.”
- Bilateral relationship as a “a partnership between the world’s oldest democracy [Greece] and the world’s largest democracy [India].”
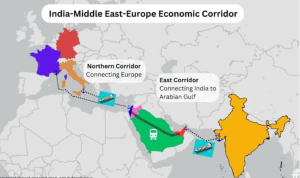
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- It is a planned economic corridor that aims to bolster economic development by fostering connectivity and economic integration between Asia, the Persian Gulf and Europe.
- Launched in September 2023 during India’s G-20 chairmanship.
Prelims Connect:
- Haifa port – Israel ;
- Piraeus Port – Greece
Indo-Pacific Oceans’ initiative(IPOI)
- IPOI is a multi-dimensional maritime cooperation framework launched by India in 2019.
- Aim: To promote a stable, peaceful, and prosperous Indo-Pacific region through collaborative efforts in various maritime domains.
Raisina Dialogue:
- Raisina Dialogue is India’s annual flagship conference on geopolitics and geo-economics, committed to addressing the most challenging issues facing the international community.
- The conference is hosted by the Observer Research Foundation in partnership with the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India.
- Attended by leaders in politics, business, media, and civil society.
Source: The Hindu
Manipur HC withdraws contentious part of the order on ST tag for Meiteis
Syllabus: GS-I
Subject: Society and Social Justice
Topic: Welfare schemes, mechanisms and institutions related to STs,
Issue: Scheduled Tribes List
Context: Manipur High Court ordered removal of a paragraph of its previous judgement, which instructed the Manipur government to consider the inclusion of Meiteis in the list of Scheduled Tribes.
Background:
- In March 2023, Manipur High Court had asked the state government to consider inclusion of the Meetei/Meitei community in the Scheduled Tribe list.
- This direction might have triggered the ongoing ethnic conflict between the Meiteis and the tribal Kuki-Zo communities in the State.
Article 342:
- Power of the president to issue by public notification, the list of Scheduled Tribes.
- Parliament has the power to make inclusions/exclusions from such a list.
+1 Advantage
Related Case Law: State of Maharashtra versus Milind,2000
“It is not open to State governments or courts or tribunals or any other authority to modify, amend or alter the list of Scheduled Tribes specified in the notification issued under Article 342” – Supreme Court.
Therefore, neither the High Courts nor the Supreme Court has the directory or advisory powers regarding Article 342.
The error in the earlier judgement of Manipur High Court is being corrected now.
Procedure of inclusion/exclusion:
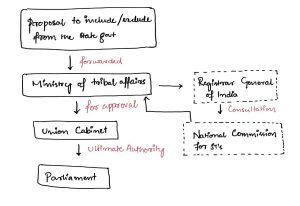

Source: The Hindu
100% FDI to be allowed in space sector: Centre.
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy
Topic: Investment models
Issue: Foreign Direct Investment
Context: The Union Cabinet took the decision to amend the existing Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy on the space sector.
Synopsis:
- Out of the 100% FDI, up to 74% FDI is under the automatic route and beyond it under the government route.
Aims:
- To attract potential investors to invest in Indian companies in space.
- Increased private sector participation would help to generate employment.
- To enable modern technology absorption and make the sector self-reliant.
- Integrate Indian companies into global value chains.
+1 Advantage
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
It refers to an investment made by a company or individual of one country into business interests locate d in another country.
Key characteristics of FDI:
- Controlling ownership of a business entity.
- Typically a long-term
- Substantial investment – significant amount of money.
India gets FDI through two routes:
- Automatic route: Under this route, the company does not require a prior approval from the RBI or the government of India.
- Government route: Under this route, the government’s approval is mandatory.
Source: The Hindu
