

GM crops will make edible oil cheaper: Govt.
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Environment, Agriculture and Science and Technology.
Topic: Introduction of GM crops
Context: Centre stressed the benefits of GM Mustard in Supreme Court against a PIL filed to stop commercial release of DMH-11.
Synopsis:
- Indigenous GM mustard meant to make edible oil cheaper, reduce imports and ensures increased yield per hectare of 25% to 30%
- The govt argued that it has the duty to protect fundamental right of people to access basic food consumed every day at a cheaper price.
Background: DMH-11:
- DMH-11 is a hybrid variant of mustard developed by cross between two varieties: Varuna and Early Heera-2.
- Barnase and Barstar are two genes from two soil bacterium introduced to enable the crossing (naturally not possible)
- Hence it is a transgenic crop.
Benefits:
- DMH-11 has 28% higher yields.
- Reduction in imports. Currently, 54% of the total edible oil demand is met through imports.
- GM mustard plants may dissuade bees from pollinating the plant and this could have knock-off environmental catastrophes.
- GM mustard hasn’t been evaluated as a herbicide tolerant crop, though it is tolerant to a herbicide called glufosinate-ammonium, posing potential risks.
Regulation:
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) under Ministry of Environment is India’s apex regulator of genetically modified plants and food products.
- The final decision on commercial release is taken by MoEFCC.
- Though GEAC has cleared the environmental release of GM mustard, the process stalled after a case was lodged in the Supreme Court.
Other GM crops allowed for cultivation in India:
- BT cotton remains the only GM crop allowed to be cultivated in India.
- Bt Brinjal, the first transgenic food crop, was cleared by the GEAC in 2009 but was put on hold by the then-UPA government.
Source: The Hindu
How satellites track the weather
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Developments and their Applications in Everyday Life
Context: India Meteorological Department (IMD) report of a high likelihood of “very dense fog” in Haryana, Chandigarh, and Delhi.
Synopsis:
- IMD has used maps from the INSAT 3D and INSAT 3DR satellites.
- Both satellites use radiometers to make their spectral measurements.
- A radiometer is a device that measures various useful properties of radiation like temperature and electrical activity.
- The INSAT (Indian National Satellite System)
- series of multipurpose geostationary satellites launched by ISRO
- For weather monitoring, forecasting and warning services (meteorology), telecommunications, broadcasting, and search and rescue operations.
- Kalpana-1 is an exclusive meteorological satellite launched by PSLV in September 2002. Deactivated Kalpana 1 in 2017.
Conclusion: ISRO is expected to launch the INSAT 3DS meteorological satellite in 2024 which will further improve the weather forecasting and warning capabilties in India.
Source: The Hindu
India’s domestic air passenger traffic to touch 300 million by 2030: Civil Aviation Minister
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Indian Economy and Development
Topic: Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
Context: Union Civil Aviation Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia addressed the inaugural session of Wings India 2024 conference.
Synopsis:
- Domestic air passenger traffic is expected to touch 300 million by 2030 from 153 million in 2023 highlighting the need to improve infrastructure.
- India became the largest purchaser of aircraft in the world after the US and China.
- However, India remains one of the most under-penetrated markets in civil aviation sector.
Conclusion: Creating capacities, removing bottlenecks and simplifying procedures will facilitate growth of the sector.
Statement/Quote: “Our resolve is not to be regulatory in nature, but to be facilitative,” – Union Civil Aviation Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia
Source: The Hindu
Amid diplomatic row, Jaishankar holds talks with Maldives foreign minister on withdrawal of Indian troops from the island
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: India and its neighborhood- relations.
Issue: India-Maldives Row.
Context: Discussions on the withdrawal of Indian military personnel, as well as expediting the completion of ongoing development projects in the Maldives, and cooperation within SAARC and NAM.
Background:
Steps taken by Maldives after Mr. Muizzu came into Power:
- Choosing Turkeyfor his first official visit as a foreign destination, unlike past Maldivian Presidents.
- Absence from the meeting of the NSA-level Colombo Security Conclave(Member-state- India, Sri Lanka, Maldives and Mauritius).
- Vow to change the Maldives’s ‘India First’ policyadopted under his predecessor and remove Indian military personnel from the island nation.
- Decided not to renewthe hydrography cooperation agreement with India after its expiry on 7 June 2024.Top of FormTop of Form
Way Forward:
Diplomatic engagement and open communication to address concerns and foster understanding.
Source: Indian Express
China, Philippines agree to lower tensions on South China Sea confrontations
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: South China Sea, Nine-dash line
Issue: China- Philippines agreement over South China sea.
Context: China and, the Philippines ease tensions in the South China Sea after confrontations, and agree on diplomacy.
Contesting Claims Over Islands:
- Ren’Ai reef (Ayungin Shoal/Thomas Shoal) a key concern.
- Disputed islands: Paracel (China, Taiwan, Vietnam), Spratly (China, Taiwan, Vietnam, Brunei, Philippines), Scarborough Shoal (Philippines, China, Taiwan).
Its impact on India and other parts of the world:
- The South China Sea is crucial as $200B Indian trade passes though
- Importance for regional stability, peace, and secure sea routes.
- Strategically vital as a link between the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
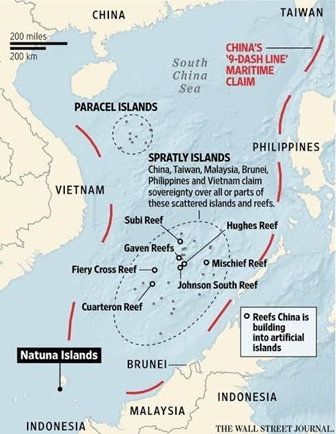
Note: The nine-dash line is a set of line segments on maps that represent the claims of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) in the South China Sea. The line is also known as the eleven-dash line, the U-shaped line, and the dotted line.
Source: The Hindu
Daily Editorials
Explained: Iran, Pakistan, and the Baloch militancy
Source: Indian Express
Subject: International relations
Topic: International Relations and Terrorism
Issue: Pakistan Iran relation
Why in news: Iran and Pakistan have attacked militant bases in each other’s territory, but also reaffirmed their commitment to good neighbourly ties.
- Recently the relationship between Iran and Pakistan has taken serious hits after they have attacked militant bases in each other’s territory.
Relationship between Iran and Pakistan:
- A) Phase I (before 1979 (Islamic revolution of Iran)):
- Both countries were firmly allied to the United States ,
- In 1955, both joined the Baghdad Pact, later known as the Central Treaty Organization (CENTO), a military alliance modelled on NATO.
- Iran provided material and weapons support to Pakistan during its 1965 and 1971 wars against India.
- The Shah of Iran criticized the liberation of Bangladesh.
- B) Phase-II (After 1979 Islamic revolution of Iran)
- The two countries found themselves at opposite ends of the sectarian divide.
- Geopolitical differences also emerged.
- There were attempt to reconcile with Iran during Benazir Bhutto’s(1995) and Asif Ali Zardari’s regime.

(Image Courtesy-BBC)
Common Baloch problem between Iran and Pakistan:
- Iran-Pakistan share 909 Kilometer long border along Goldsmith Line.
- Ethnic Baloch live on either side of the line, in the Pakistani province of Balochistan, and the Iranian province of Sistan and Baluchestan.
- And some population aslo live in the neighboring areas of Afghanistan in the north.
- Baloch share cultural, ethnic, linguistic, and religious links that transcend modern borders.
- They also nurse deeply rooted grievances against both the Pakistani and Iranian states.
- Iran and Pakistan have earlier cooperated to combat the Baloch insurgency.
- At the same time, the insurgency has been a source of tension, with the two countries accusing each other of harboring and supporting terrorists.
Conclusion:
- India has described the strikes as the matter between the two countries.
- At the same time India has mentioned its uncompromising position of zero tolerance towards terrorism.
Source: Indian Express
Competition Commission of India and the commitment to shaping a fair market environment
Source: Indian Express
Subject: Governance
Topic: Accountability
Issue: Regulatory organization- Competition Commission of India
Context: CCI reaffirms its commitment to steering India’s economic journey towards a future that is competitive, inclusive, and resilient
Approach of CCI:
- Enforcement actions -to address potential anti-competitive practices by issuing suitable punitive and remedial solutions.
- Advocacy measures – to foster a culture of competition in the markets and to nudge market participants towards competition compliance.
Mandate of CCI:
- Elimination of practices having adverse effects on competition,
- Promotion and sustenance of competition,
- Protection of consumer interests,
- Ensuring freedom of trade
- Examines the conduct of dominant companies to ensure they do not abuse their position.
- Practices like predatory pricing, denial of market access, and exclusive agreements are scrutinized to maintain healthy competition.
- CCI review any kind of merger or acquisition to avoid any harm to the competitive environment by:
- Setting prices unfairly,
- Limiting choices for consumers,
- Alternatively, stifling innovation by making it harder for smaller competitors to survive.
New age challenges to CCI and its approach to address these challenges:
- Digital economy, characterized by the dominance of a few tech giants, presents unique challenges such as vast resources and data control.
- Approach to addressing new-age challenges is multifaceted, involving regulation, advocacy, and international cooperation.
The way ahead:
- CCI’s focus should be on building resilience and agility in our regulatory practices.
- CCI should be proactive in identifying potential market disruptions and swift in our response to ensure that competition remains vibrant and fair.
- Investing in research, building expertise in new-age markets, and leveraging technology for efficient enforcement should be key to CCI’s strategy.
| Facts for prelims:
· Competition Commission of India is a statutory organization under competition commission act. · Established by the Central Government with effect from 14th October 2003. · CCI consists of a Chairperson and 6 Members appointed by the Central Government. |
Source: Indian Express
Indian Media: Quo Vadis?
Source: The Hindu
Subject: Governance
Topic: Accountability
Issue: Free media to ensure accountability
Context: The Fourth Estate having slipped from its true place in a democracy is a serious concern and there’s much to do to set things right again.
Synopsis:
- Various issues such as economic growth, the freeing of broadcast media from government control and the internet have transformed media since 1991.
- This has led to an explosion of media in terms quantity and style.
Key issues with the current functioning of media:
- “Breaking news” culture and the search for the villain of the day.
- The audiovisual media today serves simultaneously as witness, prosecutor, judge, jury and executioner.
- Social media, with its culture of unverified “fact” and viral opinion, compounds the problem.
- Print Media is also affected by this culture now feel pressed to publish without the traditional recourse to fact-checking.
- The distinctions among fact, opinion and speculation, reportage and rumor, sourced information and unfounded allegation have completely blurred.
Significance of a free and well-functioning media:
- Free media are the lifeblood of our democracy.
- Media provide the information that enables a free citizenry to make the choices of who governs them.
- Media ensures that those who govern will remain accountable to those who put them there.
- Government needs a free and professional media to keep it honest and efficient, to serve as both mirror (to society) and scalpel (to probe wrongdoing).
The way ahead:
- Engender a culture of fact-verification and accuracy.
- Insist on better journalistic training at accredited media institutes that emphasize values of accuracy, integrity and fairness in their students.
- Ensure different perspectives in newsrooms and not allow them to become echo chambers forcing an opinion onto their viewer
- Introduce laws and regulations that limit control of multiple news organizations by a single business or political entity
- A single overseer for print and television news companies, as recommended by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India and the parliamentary Committee on Information Technology.
Source: The Hindu
Smaller citizens: On the gaps in India’s education system
Source: The Hindu
Subject: Social Justice
Topic: Education
Issue: ASER 2023: Beyond Basics report
Why in news: Recently released Annual Status of Education Report, titled ‘ASER 2023: Beyond Basics’
Synopsis:
- Civil society Organisation Pratham released Annual Status of Education Report, titled ‘ASER 2023: Beyond Basics’.
- Based on survey among rural students aged 14 to 18 years.
- Conducted in 28 districts across 26 States and assessed the foundational reading and arithmetic abilities of
Data Points:
- More than half struggled with basic mathematics, a skill they should have mastered in Classes 3 and 4.
- About 25% of this age group cannot read a Class 2 level text in their mother tongue.
- Boys are doing comparatively better in both arithmetic and language,
- 8% in the 14-18 year age group are enrolled in an educational institution,
- Enrollment rate decline with increase in age9% of 14-year-olds are not in school and 32.6% for 18-year-olds are not in school.
- In class-11, most of the student opt for humanities.
- Gender based enrollment gap in science in class 11 with only (28.1%) girls compared with boys (36.3%) are enrolled.
- Only 5.6% have opted for vocational training or other related courses.
- Children opting for private tuition nationwide went up from 25% in 2018 to 30% in 2022.
- 90% of the youngsters surveyed have a smartphone; however, most of them are unaware of online safety settings.
| “Achieve universal foundational literacy and numeracy in primary school by 2025”– The National Education Policy 2020 |
Analysis:
- The trends highlight the lag in reading and solving simple arithmetic.
- The report highlights that all States have made a major push in foundational literacy and numeracy under the NIPUN Bharat Mission.
- However, the numbers show that in a diverse and vast country such as India, there is a lot of catching up to do.
- Rising enrollment is good (up to 8th) , however children are not able to cope up with the curriculum of higher classes due to low foundational skill.
- To cure the current issue we need to implement The Right to Education Act, 2009 in the true spirit of the law.
Source: The Hindu
