GAIL eyes stake in assets abroad
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy
Topic: Infrastructure
Issue: GAIL
Context: GAIL (India) Limited is seeking stakes in gas-producing assets abroad as part of India’s energy security efforts.
Prelims Connect (Institution in News)
| GAIL India :
1. Established in 1984 by the Indian government under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Ministry, operates as a Public Sector Undertaking (PSU). 2. It stands as the foremost entity in India for refining and handling natural gas, contributing significantly to the country’s energy sector. 3. GAIL is listed on both the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), demonstrating its prominent position in the financial market.Top of Form |
FMCG Companies to use Artificial Intelligence, for consumer behaviour insights.
Description:
FMCG are products that are sold quickly at relatively low prices, typically with a short shelf life.
Examples: food and beverages.
(For mains)
- The FMCG sector is the 4th largest in India, dominated by Household and Personal Care products.
- Government initiatives:
- 100% FDI in food processing, single-brand retail.
- 51% in multi-brand retail, aiming to enhance employment, supply chains, and brand visibility in organized markets.
- Key government measures include the Consumer Protection Bill, GST implementation, reducing tax rates for FMCG products and modernizing logistics and warehousing.
Source: Mint
Army outsourcing ‘essential responsibilities’ to optimize manpower
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Security
Topic: Defence related policies and new technologies.
Issue: Defence Policies
Tags: #Indian Army #Outsourcing #Essential Responsibilities.
Context: The Indian Army is outsourcing essential tasks to optimize manpower and sharpen operational effectiveness.
- Outsourced responsibilities include defense training, security, equipment repair, and facility management.
- No core functions are outsourced without approval from the Vice Chief of the Army.
+1 Advantage For Mains:
| ü It signifies a shift in perception, as defense was previously considered strategic and exempt from economic analysis.
ü Its emphasis on outsourcing reflects both budgetary constraints and a recognition of the efficacy of private business practices in defense operations. |
Source: Indian Express
Govt. gets ready to include ASHA and Anganwadi workers/helpers in its Ayushman Bharat scheme
Syllabus: GS-I
Subject: Society and Social Justice
Topic: Social sector – Health
Issue: Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana, Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs)
Context: The central government decided to to include Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) and Anganwadi workers and helpers in the free cover for health treatment under the Ayushman Bharat Scheme.
Asha workers:
- ASHA workers are volunteers from within the community.
- They are trained to provide information and aid people in accessing benefits of various healthcare schemes of the government.
- The role of these volunteers under the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM).\
- first established in 2005.
| Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY):
AB-PMJAY: · Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) will provide a cover of up to Rs. 5 lakhs per family per year, for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization. · Nodal ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) · The cover will include pre and post-hospitalization expenses. It will also cover all pre-existing conditions.. · The scheme covers over nearly 40% of the population targeted towards poorest and the vulnerable. |
Source: The Hindu
Direct tax kitty gathers steam, up 20.25% by February 10
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy
Topic: Taxation
Issue: Direct Taxes.
Context: India’s net direct tax collections rose by 20.25%.
Prelims Connect (Terms in News):
| Personal Income Tax:
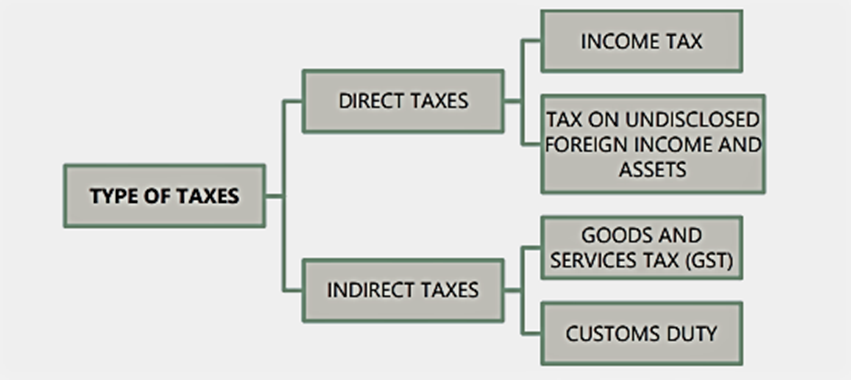
· This tax is imposed by the government on an individual’s income. · Most individuals do not pay the individual income tax on the full amount of income due to tax exemptions, deductions, and credits. Corporate Income Tax: · It is called company tax or corporation tax and is a direct tax levied on a company’s income or capital by the government. Direct Tax: · A direct tax is imposed directly upon the taxpayer and is paid by individuals directly to the Government. · The Central Board of Direct Taxes is responsible for levying and collecting. Indirect Tax: · End users pay these taxes; everyone pays the same amount of indirect taxes. · Transfer of liability is possible in indirect tax.
|
Source: The Hindu
Parliament’s average annual sitting days down to 55 in the 17th Lok Sabha from 135 in the first
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Polity
Topic: Legislature
Issue: Sessions in Parliament.
Context: The average annual sitting days of the 17th Lok Sabha, are only 55 days on average, whereas the first Lok Sabha sat for 274 days.
| Parliamentary Sessions in India:
1. India does not have a fixed parliamentary calendar. By convention (i.e. not provided by the Constitution), 3 sessions are held per year. 2. The President summons each House of the Parliament from time to time. The gap between the two sessions of the Parliament cannot exceed 6 months. |
Source: The Hindu
Daily Editorials
A privileged strategic partnership, without a gulf
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: India’s relations with other nations
Issue: India – UAE
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
India- UAE relationship:
- Climate issues:
- India and the UAE co-launched the Global Green Credit Initiative at the COP28 climate summit.
- Economic partnership: Bilateral trade grew to $85 billion in 2022-23 making UAE,
- India’s third-largest trading partner.
- India’s second-largest export destination.
- The fourth-largest overall investor in India.
- The India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement.
- Fintech:
- RuPay card, a key component of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), is accepted in the UAE.
- The rupee is being accepted for transactions at Dubai’s airports.
- Both countries operationalised a rupee-dirham settlement system (Indian Oil Corporation made a rupee payment to the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company for crude oil imports)
- Energy security:
- UAE is the only nation from West Asia which has strategic oil reserves stored in India.
- Strategic ties: both countries are part of important groupings such as..
- I2U2 or the West Asian Quad (India, Israel, the United States and the UAE).
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC).
- Instances highlighting the good relations between India and UAE:
- In 2018, India was the ‘Guest of Honour’ country at the UAE’s annual cultural festival.
- Modi was conferred the UAE’s top civilian honour, the Order of Zayed.
- Sheikh Mohammed Bin Zayed Al Nahyan (Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi) was the chief guest at the Republic Day parade in Delhi in 2017.
- The IIT Delhi Abu Dhabi campus has been established.
- The UAE opened a consulate in Hyderabad.
- Conclusion: India recognizes and values the UAE’s role in the region, the UAE is also aware of the ‘global leadership’ role that India is set to acquire.
Prelims Connect:
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): is a combination of open technology standards built for
(i) public interest,
(ii) enabling governance, and
(iii) a community of market players working to drive innovation, especially across public programmes.
Eg: United Payments Interface (UPI)
Aadhar Enabled Payment System etc.
Strategic oil reserves: these are stockpiles of crude oil that have already been extracted and can be readily refined into fuels like Petrol and Diesel.
Global Green Credit Initiative serves as the international platform for dialogue, collaboration, and the exchange of innovative environmental programs and instruments.
Source: The Hindu