

Centre to scrap Free Movement Regime with Myanmar, says Shah
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: India & Its Neighbouring Countries.
Issue: Free Movement Regime.
Tag: #FMR #India-Myanmar #Bordering states.
Context: India scraped FMR between India and Myanmar to bolster internal security and preserve the demographic structure of North Eastern States bordering Myanmar.
- It shares a border of 1,643 kilometres, spanning four states: Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh.
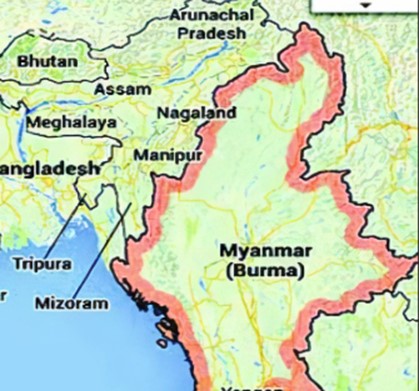
Free Movement Regime (FMR):
- Mutually agreed arrangements allow tribes living along the border to travel up to 16 km inside the other country without a visa.
- Initiated in 2018 under the Act East policy during improved diplomatic relations.
- Individuals require a border pass issued by the competent authority, valid for one year.
Act East Policy: to promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and develop strategic relationships with countries in the Indo-Pacific region.
Source: The Hindu
India-China bilateral trade hit a new record in 2023: Envoy.
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: India & its neighbourhood.
Issue: India-China relations.
Tags: #India-China #Panchsheel #Bilateral_Trade.
Context: India-China bilateral trade reached a record high in 2023, surpassing $136.2 billion despite mid-year slowdowns.Key Points:
- India’s exports to China increased by 6%.
- Despite trade growth, there’s a 16-month absence of a Chinese Ambassador to Delhi, no direct flights, and lingering tensions at the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- No direct reference was made to LAC tensions; instead, the focus was on the 70th anniversary of the India-China Panchsheel agreement, emphasizing peaceful coexistence.
Prelims Connect:
| The Panchsheel Agreement: (70th Anniversary):
Signed in 1954 between India and China, embodies five principles of peaceful coexistence: 1. Mutual respect for territorial integrity and sovereignty 2. Mutual non-aggression 3. Mutual non-interference 4. Equality and mutual benefit 5. Peaceful coexistence. · It was a key aspect of Nehru’s Hindi-Chini-Bhai-Bhai (India-China Brotherhood) agenda. · The agreement aimed to resolve disputes peacefully, but tensions resurfaced over territorial issues, leading to the 1962 Sino-Indian War. · Despite its strain, the Panchsheel Agreement remains significant in the history of India-China relations. |
Source: The Hindu
Cannot treat Scheduled Castes as a homogenous group: Supreme Court.
Syllabus: GS- III
Subject: Society and Social Justice
Topic: Welfare schemes, mechanisms,laws and institutions related to SCs
Issue: Sub-categorisation of SCs
Context: Supreme Court hearing on categorisation of scheduled castes
- Tamil Nadu urged for an updated reservation policy.
- The court noted that Scheduled Castes aren’t a uniform group, some are advancing while others remain underprivileged
- The court debates whether states can sub-categorize backward classes within SC for better reservation benefits.
Prelims Connect (Important Judgements)
Article In News: Article 341: It empowers the President of India to specify certain castes, races, or tribes as “Scheduled Castes” for the Constitution. |
Source: The Hindu
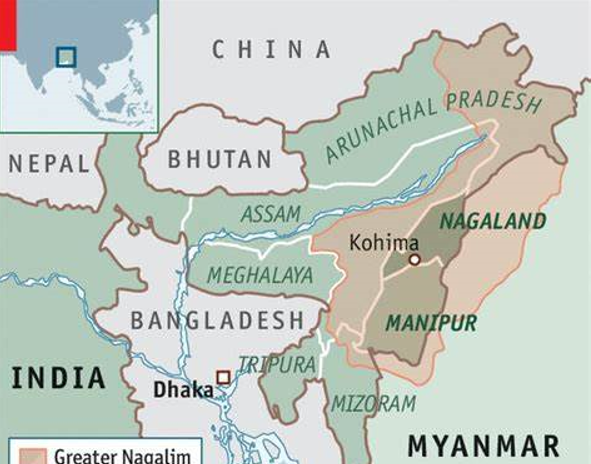
Mixed reactions in the northeast to the Centre’s decision to fence the India-Myanmar border.
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Internal Security
Topic: North -East regional issues
Issue: Fencing the borders.
Tags: #India-Myanmar #Border-Fencing #N-E states.
Context: India plans to fence its 1643 km border with Myanmar to enhance surveillance and establish a patrol track.
- Manipur, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh welcome the decision, citing security benefits and to curb illegal entry and exploitation of the Free Movement Regime (FMR) agreement.
- Mizoram and Nagaland opposed the fencing, emphasizing cultural and community ties across the border. Asserting the right of the Zo community to live without barriers between Mizoram and Myanmar.

Prelims Connect:
| Zo tribes:
· The Zo people comprise various tribes, including Chin, Kuki, Mizo, Lushei, Zomi, and others, spread across Myanmar, India, and Bangladesh. · The tribes share a common history, including migration and settlements in different regions, and are connected by their Christian faith.
|
Source: The Hindu
India to exclude non–trade issues at WTO talks, to engage with EU on CBAM.
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy;
Topic: Trade & External sector ( WTO &Issues).
Issue: WTO.
Context: India to focus on trade-centric discussions at the WTO conference, avoiding non-trade issues like labour and climate.
Key Points for Discussion:
- India is actively engaging with the EU regarding the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) to protect its industries from adverse effects.
- It opposes unilateral environmental policies like the EU’s carbon tax and deforestation laws, which it believes could harm international trade dynamics.
- India suggests discussing social issues like women’s economic empowerment in UN-specific forums rather than at the WTO to prevent impacts on its WTO rights and obligations.Top of Form
| CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism): CBAM aims to prevent carbon leakage, ensuring fair competition globally. It imposes carbon prices on imports, encouraging emission reduction and cleaner production while generating revenue for climate policies. |
Source: Mint
Rs. 4797 cr PRITHVI to boost atmosphere, polar, and ocean research, says Rijiju
Syllabus: GS- III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Defence Technologies.
Issue: PRITHVI Initiatives.
Context: The PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI) initiative, by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), aims to boost and maintain research momentum in various fields.
Synopsis:
- The PRITHVI initiative covers ongoing research in atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, geosphere, and biosphere until 2026.
- PRITHVI consolidates research efforts to efficiently allocate funds across different areas.
- It promotes international collaboration, allowing Indian scientists to work with global experts.
- It addresses the crucial need for understanding climate change impacts on the atmosphere, ocean, and polar regions.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences also launched the Deep Ocean Mission in 2021 with a focus on exploring minerals in the central Indian Ocean basin.
| Some of the ongoing research projects that will now fall under PRITHVI include:
1. Atmosphere and Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems and Services (ACROSS) 2. Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources, and Technology (O-SMART) 3. Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER) 4. Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE) 5. Research, Education, Training, and Outreach (REACHOUT) |
Source: The Hindu
Raising judges’ retirement age could extend service of non-performers: Justice dept. to Par Panel.
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Polity
Topic: Judiciary & Tribunals.
Issue: Retirement of judges.
Context: Report of Parliamentary Standing Committee on Law and Personnel.
The proposal to raise high court judges’ retirement age to 65 in 2010 stalled in Parliament.
Key points highlighted by the Department of Justice:
- Extending judges’ retirement age may prolong tenure for
- Risk of other sectors demanding similar age extensions.
- Retirement age raise should coincide with improved transparency in judicial appointments.
- Retirement age revision needs to address pending cases.
| Retirement of Judges:
· Currently, Supreme Court judges retire at 65, while High Court judges retire at 62. · District Court judges’ retirement age is determined by state governments. · Bills like the 114th Amendment Bill, of 2010, aim to increase the retirement age of High Court judges to 65. · There have also been suggestions by, the Venkatachalliah Committee, to raise the retirement age of Supreme Court judges to 68. |
Source: Indian Express
Daily Editorials
Winning Trust
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Polity
Topic: Executive
Issue: Regional Parties
Context: JMM party fielded Champai Soren as the CM
Highlights
- Regional parties in India are unable to evolve in to cadre based, ideology driven units
- Era of BJP dominated system in Indian politics is creating new challenges for regional parties – use of investigative agencies to weaken the leadership, defections of elected MLA, Splits ( NCP and Shiva sena in MH)
Data points
India – China bilateral trade hit a new record in 2023, says Chinese envoy
- India – china trade stands at $ 136.2bn
- Imports from china surpassed $100bn
Equity concerns in banning fossil fuel extractions
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management
Topic: Global Agreements and Efforts
Issue: Environmental Financing
- COP 26 at Glasgow emphasised on phasing out of fossil fuel subsidies and banning of the extraction of fossil fuel itself.
- India has got the word phasing out changed to Phasing down.
- fossil fuel subsidies are termed as inefficient.
Equity concerns
- developing countries are heavily dependant on fossil fuels.
- They are essential for energy security, development, employment generation and Government revenues – Ex – Azerbaijan,Nigeria, Oman, Timor Leste etc.
- Environmental impact assessment for fossil fuel extractions considering them as trans boundary resources.
- It is very expensive and difficult for developing countries.
- Phasing out of fossil fuels is not in line with common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities , Nationally determined contributions.
Downloading child pornography is an offence
Syllabus: GS-I
Subject: Society and Social Justice
Topic: Welfare schemes, mechanisms, laws and institutions related to children
Issue: child pornography
- In USA, Child sexual abuse material (CSAM) is the word used in the place of child pornography.
- India can adopt similar language to differentiate it from the generic word pornography. ( It normally implies a consented activity )
- Inconsistency exists between POCSO act and IT act. POCSO act shall be amended to make CSAM an offence under the act.
Over 20,000 FCRA licenses cancelled, most from TN
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Polity
Topic: Legal Issues
Issue: Foreign Contribution Regulation Act
FCRA stands for Foreign Contribution Regulation Act. it is tightened to regulate the floe of foreign funds to NGO’s.
- Organizations have to compulsorily register with Home ministry if they wish to receive foreign funding.
- Government monitors the expenditure to prevent any possible diversion of funds for activities detrimental to National interest.
- regulation is allegedly used to harass civil society and media houses.
Examples
- CBI investigation is initiated against – centre for equity studies, Oxfam India
- CBI conducted searches and registered a case against News click
FCRA registration cancelled for over 20,000 organisations till feb, 2024. it includes prominent organisations like centre for policy research and world vision India.
Road Map for Fiscal consolidation
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy
Topic: Fiscal policy and Budgeting
Issue: Fiscal consolidation
- Interim budget emphasised on increasing capital expenditure and fiscal consolidation.
- Capital expenditure is increased to 11.1% in the interim budget over 2023-24 . It is expected to go up to 17% in regular budget.
- Capital expenditure as % of GDP saw only a marginal increase – 3.2% in 2023-24 to 3.4 in 2024-25
- Fiscal deficit is expected to go down to 5.1%. centre’s fiscal deficit target is 3% by 2028-29
- House hold savings in financial assets is decreasing.
Estimations for 2024-25
- buoyancy of tax revenue – 1.33
- Real GDP growth rate of 7%
Committee on FRBM act, 2003
Debt to GDP ratio of centre and states put to together shall not be more than 60% and centre shall not cross 40%.
Taking Cancer On
Syllabus: GS III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Medical science and Health
Issue: Cancer Treatment, CAR T-Cell Therapy.
Context: For the first time, a patient in India become free of cancer cells after being treated with CAR T-cell therapy.
Cancer Treatment in India:
- Cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
- In India, about 8 lakh people every year are dying because of cancer.
- Traditionally cancer treatments included chemotherapy, radiation and surgery.
CAR T-cell therapy (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy):
- This therapy is customized for each patent.
- It involves extracting T cells (a type of immune system cell) from the patient and growing them in the laboratory.
- The T cells are armed against cancer via gene editing and infused back into the patient’s body.
Advantages:
- Easier for patients, when compared with chemotherapy and radiation etc.
- effective against relapse of cancer cells.
- Fortification of patient with living drug (modified T cell) to constantly fight cancer cells.
Concerns:
It is costly for a large section of population in India.
Need more research and development in the field.
Prelims Connect:
Genome editing: is a group of technologies using which the DNA of organisms (plants, bacteria, and animals etc.) is changed.
CRISPR-Cas9, TALE nucleases, and zinc-finger nucleases are some of Gene Editing technologies.
