

Rajnath Singh to visit U.K., the first by a defence minister in 22 years
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: Bilateral relations involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Context: Defence Minister Rajnath Singh will embark on a two-day visit to the U.K. to rejuvenate strategic and security ties between, including possible collaboration to jointly develop fighter jets and other military platforms.
Synopsis:
- It is expected that discussions will be on a wide range of issues in the spheres of defence, security and industrial cooperation.
- The talks would largely focus on sharing of critical technology and expanding bilateral industrial defence cooperation.
- In April 2022, Prime Ministers of both countries had agreed on a new and expanded India-UK defence partnership.
- UK also created an Open General Export Licence (OGEL) for India to “reduce bureaucracy and slashing delivery times for defence procurement”.
| India-UK relationship:
· upgraded to Strategic Partnership in September 2004 and Elevated to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2021. · Major trading partners. UK is listed 19th among the top 25 trading partners of India. · The India diaspora in UK is one of the largest ethnic minority communities in the country. Major Issues: · Free Trade Agreement (FTA) Negotiations: differences over tariff reductions, particularly in agriculture and dairy, and intellectual property rights. · Pro-Khalistan Activities in the UK · Human Rights: The UK has frequently raised concerns about human rights issues in India. · Russia-Ukraine War: This divergence in strategic views. India’s neutrality and continued imports of Russian oil, whereas UK supports Ukraine. |
Conclusion: Despite the challenges, the India-UK relationship remains strong, anchored by historical ties, shared values, and growing economic and strategic interests.
Source: The Hindu
IIT Delhi team makes first hi-res landslide risk map for India
Syllabus: GS-III;
Subject: Disaster Management;
Topic: Disaster and Disaster Management.
Issue: Land Slides Map.
Synopsis:
- The map, called as ‘Indian Landslide Susceptibility Map’, is the first of its kind by virtue of being on a national scale, leaving out no locations in the country.
- Aim: To help identify the most dangerous areas and help allocate resources for mitigation strategies better
- The map data is available for free; an online portal has also been created.
- 5 lakh landslides data was collected via the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and other sources.
- Information was gathered from across the country on 16 such factors, like soil type, tree cover, which they called landslide conditioning factors.
- The researchers said they want to build on data from the map and develop a ‘Landslide Early Warning System’ for India.
Landslides: Landslides are the mass movement of rock, soil, and debris down a slope.
Various factors causing landslides include:
- Heavy rainfall: This is the most common trigger, as water seeps into the soil, increasing its weight and reducing its cohesion.
- Earthquakes:Seismic activity can destabilize slopes and trigger landslides.
- Erosion:Undercutting of slopes by rivers or streams can weaken the support and lead to landslides.
- Changes in groundwater levels:Rapid decreases or increases in groundwater levels can destabilize slopes.
- Human activities: Deforestation, improper construction practices, and mining can all increase the risk of landslides.
Effects: Impact on the economy, damages to infrastructure, loss of life, disruption of landscapes, decline in river ecosystems, trigger floods, affect livelihoods, and impede development
Vulnerability zones:
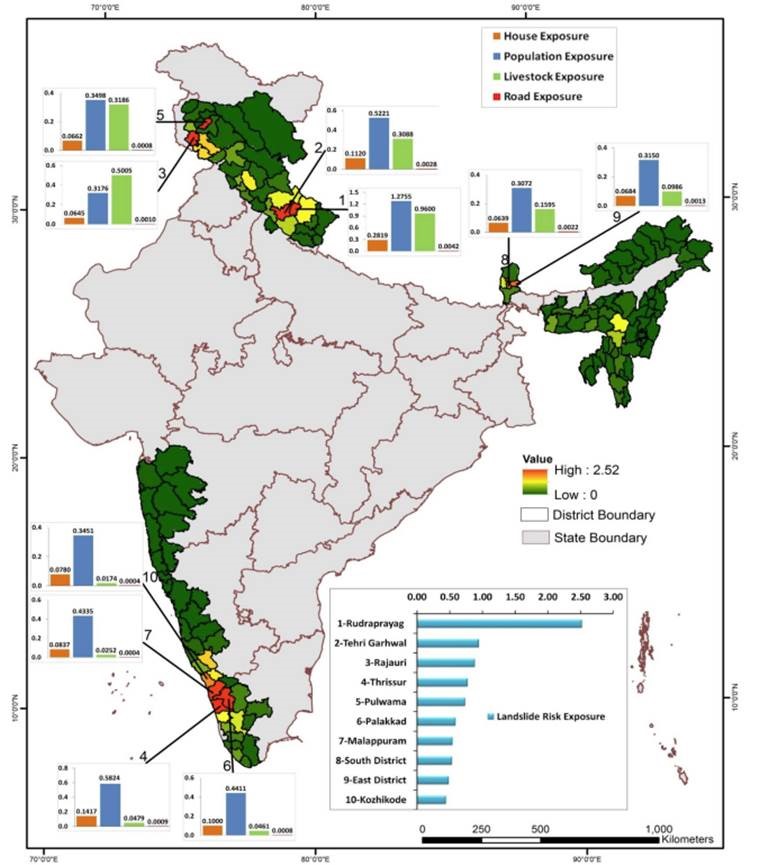
Landslides happen in very localised areas and affect only about 1-2% of the country.
- The spread of landslides in India is not uniform.
- Himalayan region – most affected.
- The Northeastern states – highly prone
- The Western Ghats states – regular landslides.
National Initiatives:
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA): Mandated to formulate policies and guidelines for disaster management.
National Landslide Risk Management Strategy: Task Force with sub-groups addressing hazard maps, monitoring systems, awareness programs, capacity building, regulations, and stabilization/mitigation.
Conclusion: This landslide vulnerability map marks a significant step forward in proactively mitigating the risk of landslides and protecting communities. By identifying areas susceptible to landslides, this map can inform crucial preventative measures, saving lives and minimizing property damage.
Source: The Hindu
IAF C-130Jmakes maiden night landing in Kargil
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Security
Topic: Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate.
Context: The Indian Air Force’s C-130J aircraft achieved a significant milestone with its successful night landing at the strategically vital Kargil airstrip in Ladakh.
Synopsis:
- This airstrip, positioned at an elevation of 9,700 feet, holds crucial strategic importance between Dras and Batalik, both major flashpoints during the Kargil conflict.
- The night landing employed terrain masking tactics, utilizing natural hills ranging from 14,000 to 15,000 feet around the airstrip to conceal movements and enhance security.
- The operation included the airlift of Garud commandos, showcasing the capability to conduct covert or clandestine missions even under the cover of darkness.
- The C-130J demonstrated its versatility, highlighting precision flying, airdrop capabilities, and the ability to operate in blackout conditions.
- The Kargil airstrip, activated in 2008, plays a crucial role in transporting troops and military equipment to forward bases in the region.
- The C-130J, part of the IAF’s fleet, operates in various capacities, including special operations, aerial refueling, search and rescue, paradrop, electronic surveillance, and weather reconnaissance.
Background
What Makes Air Force’s C-130J’s Kargil Night Landing Significant?
- The successful night landing showcases the IAF’s commitment to operational excellence and preparedness in challenging terrains, especially in the Himalayan region.
- The airstrip’s strategic importance is further emphasized by its role in transporting troops and military equipment to forward bases in the challenging terrain of Ladakh.
- The use of the C-130J for night landing signifies the IAF’s enhanced capability to conduct clandestine or covert operations even under the cover of darkness.
- Terrain masking tactics, employing natural hills ranging from 14,000 to 15,000 feet around the airstrip, were used during the night landing to conceal the aircraft’s movement.
- Terrain masking is a crucial tactic that involves hiding from enemy radar by utilizing natural or man-made terrain to block the line of sight.
- The exercise “dovetailed” with a training mission for the Garud commandos, highlighting the seamless integration of tactical training with operational maneuvers.
Conclusion: The success of the mission underscored the Indian Air Force’s commitment to operational excellence and preparedness in challenging Himalayan terrains.

Source: The Hindu
29,273 bogus firms, GST evasion of Rs 44,015 crore detected since May’ 23
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy & Development
Topic: Government Budgeting
Issue: GST Evasion.
Context: GST authorities expose 29,273 bogus firms, evading Rs 44,015 crore since May ’23; Maharashtra and Delhi top the list.
Synopsis:
- 29,273 bogus firms uncovered for GST evasion of Rs 44,015 crore since May ’23.
- Maharashtra tops with 926 bogus firms evading Rs 2,201 crore; Delhi reports higher evasion at Rs 3,028 crore by 483 firms.
- Haryana leads fake firms per lakh registered firms, followed by Delhi, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra.
- Oct-Dec ’23: 4,153 bogus firms found evading Rs 12,036 crore in input tax credit.
- Central GST authorities detect 2,358 bogus firms, protecting revenue of Rs 1,317 crore.
- Special drive since May ’23 exposes 29,273 bogus firms, saving Rs 4,646 crore.
- Measures include biometric-based Aadhaar authentication, sequential filing of GST returns, and data analytics for fraud detection.
Background:
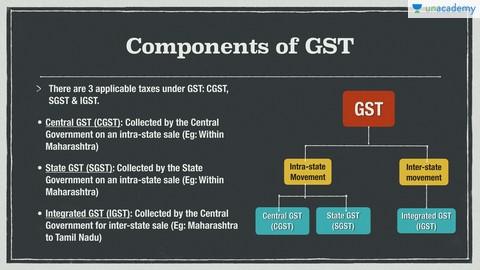

A value-added tax for domestic consumption, impacts the supply side, employs destination-based taxation, and has dual GST with multiple rates. Legislative basis lies in the 2016 Constitution (101st Amendment) Act.
For trade and industry, it simplifies the tax regime, eases business, and increases competitiveness. Consumers benefit from transparent prices and potential reductions. States experience an expanded tax base, economic empowerment, and increased compliance. Exemptions include customs duty on imports, petroleum, tobacco products, excise duty on liquor, stamp duty, and electricity taxes.
The GST Council, chaired by the Union Finance Minister, oversees tax reforms. It creates a unified market, reduces corruption, and stimulates the secondary sector
Conclusion: The continuous evolution of the GST system and the emergence of new evasion methods necessitate constant vigilance, adaptivity, and a commitment to ongoing reforms.
Source: Indian Express
No local body representatives in J&K from January 9; no Assembly since 2018
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Governance
Topic: Devolution of powers and finances up to local levels.
Issue: Local Body Elections.
Context:
As of January 9, 2024, Jammu and Kashmir will lack local body representatives, with the five-year term of nearly 30,000 panches and sarpanches coming to an end.
Top of Form
Synopsis:
- Almost 30,000 Panches and Sarpanches five-year terms expire on this date.
- No Assembly representation in J&K since 2018. Panchayat elections were last held in late 2018.
- Next local body elections were delayed due to a delimitation exercise. Which initiated on December 28, 2023.
- Concerns were raised about the lack of grassroots representation.
- J&K under Central rule since June 2018 after the BJP-PDP coalition collapse.
- Union Home Minister indicates statehood restoration after Assembly elections.
- Supreme Court directs J&K Assembly elections by September 30, 2024.
- Delimitation commission highlights population-based funding concerns during the redrawing of boundaries.
- The Union government transferred subjects to panchayats in 2018, affecting local governance.
Background
| Local Body Election:
· Local Body Elections (India) are elections conducted to elect local body representatives in India as per the provisions of 73rd and 74th Amendments of the Constitution of India in states and union territories of the country. · These elections are conducted periodically by State Election Commissions as per the procedures laid down in State laws. · The objective of forming these local bodies is to decentralize the process of democracy and devolve power at local levels. · Local Body Elections are performed at different levels based on the local population, such as Municipal Corporations, Municipality Elections, Nagar Panchayat, Zila Parishad Elections, Village Panchayat Elections, and Panchayat Samiti Elections. · India has one of the largest democracies with 3.1 million elected representatives, out of which 1.3 million representatives are women in 2,50,000 government bodies. · However, these local governance systems face several challenges such as lack of support from the government, non-functional institutional organizations, and restricted efforts on education of elected representatives. |
Conclusion: Jammu and Kashmir faces a governance void as local body terms end, with uncertainty over elections due to the ongoing delimitation, impacting grassroots representation and financial disbursements.
Source: The Hindu
