

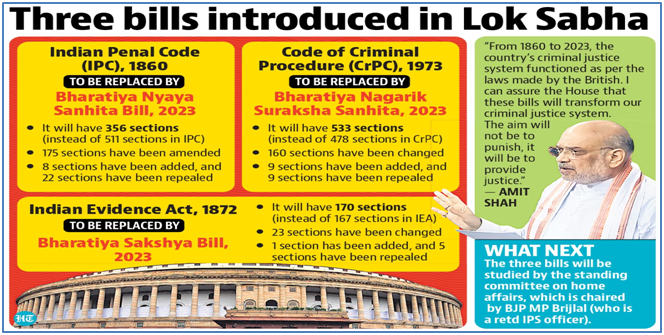
Roll-out schedule of 3 new criminal codes will be notified by January 26
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Governance
Topic: Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions
Context: It will take nine months to a year for the three criminal laws to be implemented across the country, and a pilot project is all set to begin in Ahmedabad in the next two months.
Synopsis:
- The implementation date for three new criminal codes, replacing existing laws, will be notified before January 26.
- The plan includes training 3,000 master trainers to educate police personnel in a pyramid setup reaching each district.
- The integration of various criminal justice system modules aims to create a faster system, focusing on scientific investigation and forensics-based approaches.
- The new laws will replace the Indian Penal Code, Indian Evidence Act, and Code of Criminal Procedure.
Source: The Hindu
Truckers strike: The Home Ministry seeks to pacify truckers protesting the new hit-and-run law
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Governance
Topic: Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions
Context: Transporters, protesting the new hit-and-run law, went on a nationwide strike. The Ministry of Home Affairs assured the All India Motor Transport Congress (AIMTC) that decisions on stringent provisions would be taken after consultation.
Synopsis:
- The apprehensions among vehicle drivers regarding provisions of 10-year punishment and fine provided for in Section 106 (2) of the Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita.
- Currently, as per Section 304A (causing death by negligence) of IPC, drivers in rash and negligent cases face penalties of up to two years.
- The new law
- The issue arose due to concerns about potential misuse and harsh punishments in the new provisions prescribing up to 10 years’ imprisonment for drivers in hit-and-run cases.
What is Section 106(2), BNS?




Source: Indian Express
Coal output growth slid to a six-month low in December
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science and Technology
Topic: Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology; Indigenization of Technology and Developing New Technology crossed
Context: In December 2023, India’s coal output growth hit a six-month low of 10.75%, reaching nearly 93 million tonnes.
Synopsis:
- This decline in coal production is reflected in the Index of Core Industries, where coal holds a weightage of over 10%.
- The core sectors, constituting 40% of the Index of Industrial Production (IIP), had grown 12% in October but slid to the lowest levels since March 2023 in November.
- Despite slower year-on-year growth in coal dispatches, the December numbers, showing a 5.6% increase from November, suggest a potential rebound in electricity generation, a critical component of the core sectors’ index.

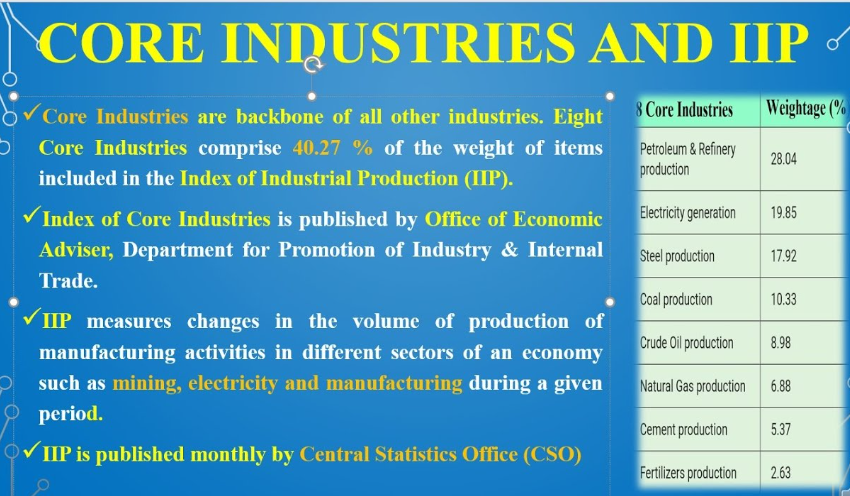
Conclusion:
India’s coal output growth hit a six-month low at 10.75% in December, nearing 93 million tonnes. Despite slower growth, a 5.6% increase in coal dispatches suggests a potential rebound in electricity generation.
Source: The Hindu
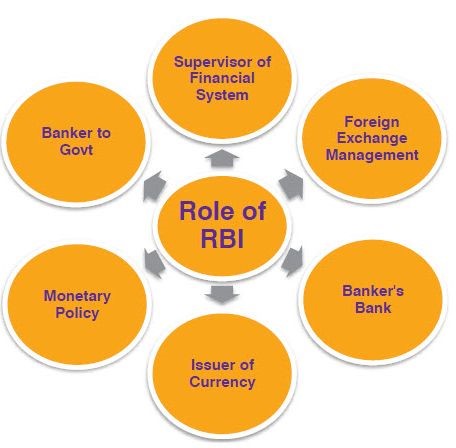
Inoperative & unclaimed accounts: How will the RBI’s revised guidelines benefit customers?
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Indian Economy
Topic: Government Budgeting.
Context: The RBI has asked banks to undertake at least an annual review in respect of accounts, where there have been no customer-induced transactions for more than a year.
Synopsis:
- The RBI’s revised guidelines allow customers to reactivate inoperative accounts/unclaimed deposits by submitting fresh KYC documents at any bank branch.
- An account is deemed inoperative if no customer-induced transactions occur for over two years.
- The RBI instructs banks to conduct an annual review and communicate inactivity to account holders. Unclaimed deposits, inactive for ten years, are to be classified as such.
- Banks should segregate zero balance accounts for government beneficiaries. Reactivation is facilitated through KYC updation, including a video-CIP option.
- Banks cannot charge for reactivation, penalize for non-maintenance of minimum balances, and must continue interest payments on savings accounts.



Source: Indian Express
Higher borrowing by states to widen yields spread with G-Sec
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economic Development
Topic: Government Budgeting.
Context: States’ borrowing seen at record Rs 4.13 lakh crore in Q4
Synopsis:
Overview:
- In Q4, Indian states, including Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Bihar, plan to borrow a record Rs 4.13 lakh crore, widening the yield spread with central government securities.
This surge in state borrowing is anticipated to raise concerns over increased supply of dated securities, leading to a potential rise in borrowing costs.
- The 10-year state government securities’ spread over the benchmark 10-year G-sec reached 53 bps, the highest since January 2022. Economists predict a further widening of spreads due to concentrated supply in the 15-year to 50-year segment.
- The actual borrowing may vary from the proposed amount, influenced by capex loan schemes and tax devolution.
Background
| What are govt securities?
Government security (G-Sec) is a tradeable instrument issued by the central government or state governments. Key features: · Government securities acknowledge debt obligations, with short-term options like treasury bills (less than a year) and long- term choices such as government bonds or dated securities. · Central and state governments issue these, the latter known as state development loans. As government-backed instruments, they are risk-free. Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) can participate within set limits. |
Conclusion: Concentrated supply in longer-tenure securities raises concerns over borrowing costs, while actual borrowing may vary due to capex schemes and tax devolution.
Source: The Hindu
Govt, ready with rules for CAA, set to be notified before LS polls announcement
Syllabus: GS-II:
Subject: Polity & Governance
Topic: Constitution of India —historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions, and basic structure.
Context: Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) the Bill for which was cleared by Parliament in December 2019, will be notified much before the announcement of the Lok Sabha elections,
Synopsis:
- The Indian government is set to notify rules for the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) before the announcement of Lok Sabha elections.
- The CAA, passed in December 2019, aims to grant Indian citizenship to certain religious minorities from Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh.
- The rules, now ready, will facilitate online application submission through a dedicated portal. The move follows several extensions and is seen as addressing the prolonged delay in implementing the contentious legislation, which sparked nationwide protests.
- The rules include declaring entry years and don’t seek documents for applicants post-2014. The government assures the process will be transparent and online.
- What is Citizenship Amendment Act, (CAA) 2019?
- The Citizenship Amendment Act, 2019 seeks to provide Indian citizenship to illegal refugees from 6 communities coming from Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Afghanistan.
- These 6 communities include; Hindu, Buddhist, Sikh, Christian, Jain, and Parsi.
- Worth to mention that Illegal migrants can be imprisoned or deported under the Foreigners Act, 1946 and the Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920. These two Acts empower the central government to check the entry, exit and residence of foreigners within India.


Source: Indian Express
Centre plans to end Free Movement Regime with Myanmar to check influx of illegal migrants, and insurgents
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Security
Topic: Security challenges and their management in border areas.
Context:
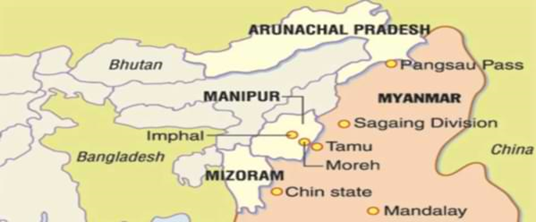
India ends visa-free movement with Myanmar along a 1,643 km border, replacing it with visas. Top of Form
Synopsis:
- The Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the Myanmar border, passes through Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh,
- The FMR, allows visa-free movement within 16 km on either side.
- A 300 km stretch of the border will be fenced over the next four-and-a-half years.
- The decision aims to address concerns of insurgent activities, illegal immigration, and smuggling networks misusing the FMR.
- Manipur suspended the FMR in 2020 due to the pandemic, citing ethnic violence linked to border movement. The move follows a surge in refugees after the Myanmar military coup in 2021.
Background
Myanmar holds significance for India due to its strategic location as a gateway to Southeast Asia, countering China’s influence, and addressing internal security concerns in India’s northeastern states.
Strong economic cooperation, with India being a major trading partner and investor in Myanmar’s energy, infrastructure, and agriculture sectors, further solidifies the importance of this relationship.

The Sittwe port in Myanmar developed as part of India’s SAGAR Vision.
The historical and cultural ties between the two countries, rooted in shared traditions and the prevalence of Buddhism, contribute to a strong and enduring connection.
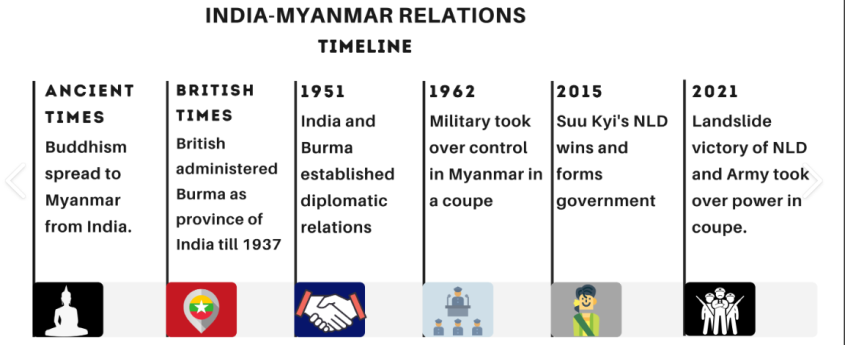

Conclusion: India’s decision reflects a strategic move to address security concerns, insurgent activities, and potential misuse of border privileges. The decision underscores the government’s commitment to safeguarding national interests and maintaining border integrity.
Source: Indian Express
