

Nearly eight million displaced by Sudan war: United Nations
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations (I)
Topic: International institutions, agencies and for a
Issue: Sudan Refugees
Context: UN High Commissioner for Refugees called for urgent and additional support to meet the needs of Sudan refugees.
- Sudan war – conflict between Sudan’s army and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces erupted in mid-April last year.
- Places in news(Prelims): Darfur region and Abyei
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees:
- Established in 1950 to address the refugee crisis that resulted from World War II.
- HQ: Geneva, Switzerland
- Mandate:
- To aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and
- To assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integration or resettlement to a third country.
- Functions in accordance with the
- 1951 Refugee Convention and
- 1967 Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees
- India is not a party to the 1951 Refugee Convention or its 1967 Protocol.
Source: The Hindu
Musk says first human has received Neuralink implant
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Bio-Technology
Issue: Brain computer interface
Context: Embedment of computer chip in the human brain.
- Neuralink, co-founded by Elon Musk, is working on linking the nervous system to computers.
- The brain computer interface is about the size of a large coin and is designed to be implanted in the skull, with ultra-thin wires going directly into the brain.
- The product is called “Telepathy” — which will enable users to control their phones or computers “just by thinking.”
| Potential Benefits
|
Potential Concerns
|
| Treating neurological disorders like Parkinson’s, epilepsy etc. | Inherent risks of infection, tissue damage, and unintended consequences of manipulating neural activity |
| Restoring lost function for individuals with paralysis or limb loss | Data privacy and security |
| Potentially augment memory and learning by facilitating information access and processing. | Profound ethical questions about free will and the potential for discrimination. |
Source: The Hindu
Bombay HC delivers split verdict on Kunal Kamra’s plea challenging changes in IT rules
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Polity
Topic: Judgements
Issue: IT Act 2000 and IT Rules 2023
Context: Bombay High Court delivered a split verdict in a petition that challenged Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023.
Information Technology Amendment Rules, 2023:
- It empowers the Centre to establish a fact-checking unit (FCU) to identify fake, false and misleading information about the government’s business on social media platforms.
- The government can then ask the platforms to remove such content/ news related.
- Failing to comply, intermediaries may lose their safe harbour status under Section 79 of the IT Act, 2000.
Petitioner’s arguments:
- Rules violate the right to freedom of speech and expression under Article 19 (1)(a) and right to practice and trade or profession under Article 19(1)(g).
Information Technology Act, 2000
It is a primary law in India dealing with cybercrime and electronic commerce.
Key Provisions:
- Key terms like “electronic record,” “digital signature,” “information technology,” etc. are defined under this Act.
- Legal recognition of digital signatures and their use for authenticating electronic records.
- Penalises various cybercrimes like hacking, data theft, and online fraud.
- Safe harbour provision: Intermediaries not liable for any third-party information, data, or communication.
- Empowers government to block information from public access under specific conditions like sovereignty and integrity of India, defence of India etc.
| Related Case Law: Shreya Singhal vs Union of India (2015)
The Supreme Court declared Section 66A of IT Act,2000 unconstitutional for being violative of Article 19(1)(a). Section 66A – criminalises sending offensive messages using a computer or any other communication device. |
Source: The Hindu
RBI curbs to render Paytm wallet and FASTag inoperative.
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy
Topic: Banking and Financial Intermediaries
Issue: Payments Banks
Context: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) imposed curbs on Paytm Payments Bank Ltd(PPBL).
- PPBL has been barred from.
- Taking further deposits or undertaking credit transactions or top-ups in any customer accounts, prepaid instruments, wallets, FASTags.
- Reasons for actions: Persistent non-compliances and continued material supervisory concerns in the bank.
- However, customers are free to withdraw or use their balances in these accounts without restrictions.
- RBI issued orders under Section 35A of the Banking Regulation Act,1949 which gives powers to issue directions on public interest/interest of banking policy.
| Payments Banks:
Introduced to promote financial inclusion by offering services to the unbanked and underbanked population, particularly in rural areas. Features: ● Basic banking services like bill payments, money transfers, mobile banking, and ATM/debit cards. ● Limited deposit amounts: Can accept deposits of up to ₹2 lakh per customer. ● No credit facilities:Cannot offer loans or credit cards. ● Regulation: ○ Registered as a public limited company under the Companies Act, 2013. ○ Regulated under the relevant provisions of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949; RBI Act, 1934 and Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007. |
Source: The Hindu
Centre’s fiscal deficit at 55% full-year target at Dec-end 2023: CGA
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economy
Topic: Fiscal Policy.
Issue: Centre’s Fiscal Deficit’s.
Context: As of December-end 2023, India’s government fiscal deficit was 55% of the full-year target, slightly lower than the previous fiscal year.
- The estimated fiscal deficit for 2023-24 about 5.9% of GDP.
- The government aims to bring the fiscal deficit below 4.5% of GDP by 2025-26, continuing its path of fiscal consolidation.
Formula’s (Prelims):
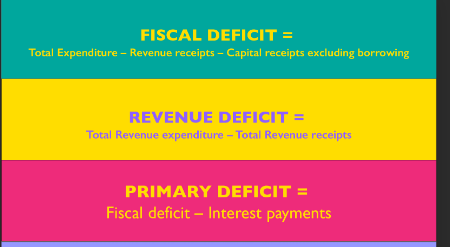
Source: Indian Express
BRICS: 5 countries officially join the Group of Emerging Nations
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: International Relations
Topic: International Institutions, agencies and fora
- New Members: Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have confirmed joining BRICS.
- Members aim to reshape what they see as an outdated world order through BRICS.
- Argentina, initially invited, has declined the invitation to join BRICS.
Take Away Notes for Mains:
| What BRICS expansion means for India:
· It offers India a platform for non-Western collaboration. · Provides avenues for cooperation with Russia and China, among others. · Emphasizes BRICS as a “non-Western” group. |
Institution in News (Prelims)
| BRICS: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, represent major emerging economies.
Aim: Focus on cooperation across economics, finance, politics, and culture, while advocating for a fairer global order. · The leadership of the forum rotates annually among the member nations, following the acronym B-R-I-C-S. · Unlike a formal organization, BRICS functions as a forum for dialogue and cooperation rather than a structured institution. · BRICS represents significant global influence, with member countries collectively accounting for 41% of the global population, 24% of global GDP, and 16% of global trade. Important Outcomes:
|
Source: Mint
The Centre plans to introduce a Bill to prevent unfair means in public examinations
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Polity
Topic: Bills/Acts/Rules.
Context: The Union Cabinet approved the draft of the Public Examination (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024. It is aimed at addressing paper leaks and organized cheating in public exams like UPSC, SSC, Railways, NEET, JEE, and CUET.
- It is proposed by the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT).
- Protection for candidates defined in the Bill.
- There is an absence of substantive national law to address exam malpractices, the Bill aims to rectify that.
Institution in News(Prelims): Department of Personnel & Training:
1. Acts as a watchdog ensuring adherence to standards in recruitment, service conditions, postings, transfers, and deputations.
2. Provides guidelines to Ministries/Departments and advises on personnel management.
3. Functions as cadre controlling authority for IAS and three Secretariat Services.
The two organizations through which the Department ensures recruitment of personnel for the Government
· Union Public Service Commission (UPSC):
· Staff Selection Commission (SSC):
Source: Indian Express
