

ISRO’s New Year launch: Special space observatory, X-ray telescope
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Achievements of Indians in science & technology;
Context: ISRO launched its first X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) on New Year’s Day using the PSLV-C58 rocket.
Synopsis:
Mission Launch:
Objective: XPoSat is a space-based observatory designed to study X-ray polarization from celestial bodies like black holes, neutron stars, and magnetars.
Global Positioning: It is only the world’s second mission of its kind; NASA launched the first, Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE), in 2021, operating in the soft X-ray band, while XPoSat operates in the medium X-ray band.
Payloads: XPoSat carries two payloads—POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays) for polarimetry and XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing) for studying the electromagnetic spectrum generated by different matter.
Development: Built entirely by two Bengaluru-based institutes—ISRO’s UR Rao Satellite Centre and Raman Research Institute—XPoSat was conceptualized in 2008, with a formal agreement with ISRO inked in 2015.
Significance: X-ray polarization measurements serve as a crucial diagnostic tool for understanding the radiation mechanism and geometry of celestial sources, providing insights into the physics of black holes, neutron stars, and active galactic nuclei.
Global Context: Worldwide, there have been only a few experiments on X-ray polarization measurements, primarily due to the difficulty in developing sensitive instrumentation. XPoSat is considered a significant step for India in this domain.
Gamechanger: XPoSat is expected to be a gamechanger in the field, as there have been limited studies in the X-ray frequency band globally, with timing, spectroscopy, and imaging being the primary focus.
Contributions: The satellite adds to India’s space-based observatories, joining the recently launched solar mission Aditya-L1 and the AstroSat launched in 2015.
Future Prospects: The launch of XPoSat is seen as a positive trend by former ISRO scientists, emphasizing the need for a regular stream of science satellites, preferably one per year, to enhance scientific research capabilities.
Source: Indian Express
Pendency down, but petitioners disappointed in many cases
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Indian Polity and Constitution
Topic: Functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary
Context: The year 2023 saw the Supreme Court hear long pending and contentious cases such as the abrogation of Article 370, samesex marriage and demonetisation.
Synopsis:
- The pendency of five judge Constitution Bench cases was reduced from 36 to 19 between January 1 to December 15.
- Dates were notified for hearing six cases before seven judge Benches and five before nine judge Benches.
- Cases of no relief to petitiners.
- In demonetisation case, the SC upheld demonetisation of 500 and 1000 currency notes with 4:1 majority, dissent by Justice B.V.Nagarathna.
- In Artice 370 case, the Supreme court evaded the basic question raised by the petitioners whether the Parliament could unilaterally extinguish the character of Statehood under Article 3 of the constitution.
- In Supriyo and others v UOI case Constitution Bench refused to legalise same sex marriage by making the Special Marriage Act of 1954 genderneutral disappointing the LGBTQ community.
- Cases where government side stepped Constitution Bench judgments.
- Anoop Baranwal case: The Central Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act of 2023 was passed modifying Anoop Baranwal judgement.
- GNCTD V UOI: Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Act, 2023, has also effectively nullified a Constitution Bench ruling in May which had upheld the authority of the Delhi government over civil services in the capital.
- Subash Desai v Governor of Maharashtra: Maharashtra Legislative Assembly Speaker Rahul Narwekar is yet to pronounce his decision on the pending disqualification petitions against the Eknath Shinde camp under the Tenth Schedule of the Constitution defying the Subash Desai v Governor of Maharashtra judgement.
Source: The Hindu
4G services will be provided at 1,117 border outposts in six years: Centre
Syllabus: GS-III.
Subject: Security
Topic: Security Challenges and their Management in Border Areas
Context: The Union government has approved 4G mobile services for more than 1,100 border outposts along India’s international borders.
Synopsis:
- The Ministry said it had signed a tripartite agreement with the Department of Telecommunications and Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited to execute the project over the next six and a half years.
- The project will cover 1,117 border outposts and intelligence posts of the armed forces and the Intelligence Bureau.
- The Ministry said that this year, 48.03 kilometres of roads had been constructed along the China border.
- After 2020 Galwan clashes, Union government approved 32 roads along the India China border.
- The first phase of the India China border road project (ICBR) was initiated in 2005 and second phase approved in September 2020.
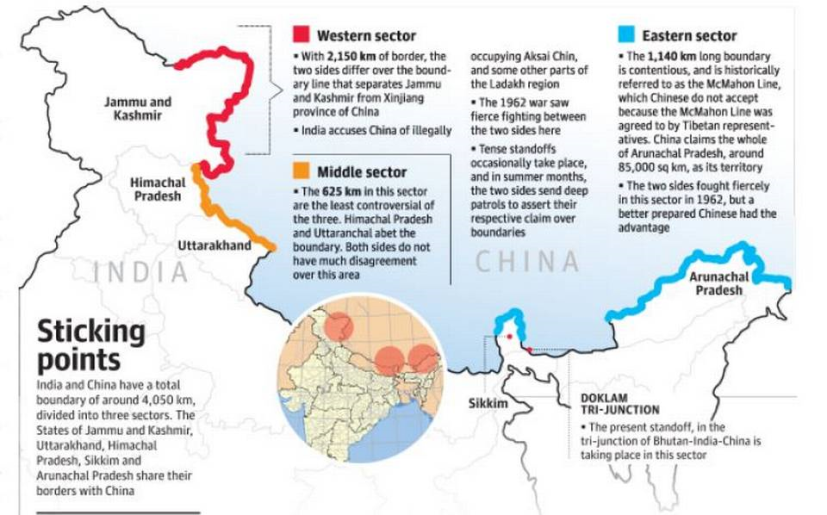
Source: The Hindu
Geelani founded outfit declared ‘unlawful body’
Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Security
Topic: Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security.
Context: The Union Home Ministry on Sunday declared Tehreek
E-Hurriyat, Jammu and Kashmir (TeH) an “unlawful association” under Section 3 of the Unlawful Activities(Prevention) Act (UAPA).
Synopsis:
- The outfit is involved in forbidden activities to separate J&K from India and establish Islamic rule.
- The group is found spreading anti-India propaganda and continuing terror activities to fuel secessionism in J&K.
- The leaders and members of the outfit had been involved in raising funds for perpetrating unlawful activities which are prejudicial to the integrity, sovereignty, security, and communal harmony of the country .
- The notification stays in effect for a period of five years.
| UAPA,1967
UAPA, passed in 1967 was aimed for the prevention of unlawful activities and associations in India. Provisions: · Defines Unlawful activity as any action taken by an individual or association intended to disrupt the territorial integrity and sovereignty of India. · Empowers central government to declare any activity or association as unlawful by an official gazette. · Highest punishment: death penalty and life imprisonment. · Applicability: Both Indians and foreigners and activites inside and outside India. |
Source: The Hindu
Aadhaar linked pay made mandatory for MGNREGS workers
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Social Justice
Topic: Welfare Schemes for Vulnerable Sections of the population by the Centre and States and the Performance of these Schemes.
Context: Wages under the MGNREG Scheme will be paid only through an Aadhaar based payment system (ABPS), which requires the Aadhaar details of workers to be seeded to their job cards.
Synopsis:
- The fifth extension of the deadline to make the system mandatory ended
- The first order to enforce the system was issued on January 30,2023, followed by extensions.
- Activists argue that mandatory ABPS led to deletion of large number of job cards leading to denial of right to work.
- LibTech India says the names of 6 crore workers have been deleted over the past 21 months.
- Union Rural Development Ministry data show that8% of the job card holders remain ineligible for this mode of payment
- The government contends that ABPS implementation will plug leaks ensure and reduce rejection.
MNREG Act,2005:
Conclusion: There must be a lenient view if linking has not been done for any genuine reason.
Panagariya to head 16th Finance Commission
Syllabus: GS-II
Subject: Indian Polity and Constitution
Topic: Appointment to various Constitutional Posts, Powers, Functions and Responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies.
Context: The Finance Ministry on Sunday notified President Droupadi Murmu’s order for Mr. Panagariya’s appointment as the chairman of 16th Finance Commission.
Synopsis:
- The commission will recommend the tax revenue sharing formula between the Centre and States for the five year period beginning April 2026.
- Panagariya, had served as the first Vice Chairman of the NITI Aayog, which replaced the Planning Commission, from 2015 to 2017.
- The names of the members of the commission will be notified separately, says the order.
- Term: Upto the date of the submission of report or October 31, 2025, whichever is earlier.
| Article 280:
· Mandates the president to constitute a finance commission every five years. · Composition: Chairman and four other members. · Includes the duty of the commission to recommend to the president. · Empowers Parliament to decide the qualifications of members to be appointed. In consonance Finance Commission 1952 Act was passed. |
Conclusion: The recommendations of Finance Commission are not binding in nature and It is up to the Union government to implement its recommendations on granting money to the states.
Source: The Hindu
