

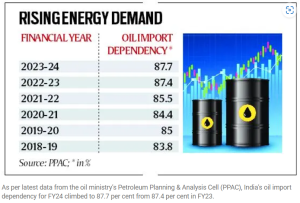
India’s reliance on oil imports hits fresh full-year high in FY24.
| Syllabus: GS-III; Subject: Economy; Topic: Trade and External sector, Issue: Oil Imports. |
Context: India’s reliance on imported crude oil hits a record high of 87.7% in FY24.
Synopsis:
- Rising demand for fuel drives increased dependency despite efforts to boost domestic production.
- Heavy reliance on oil imports impacts trade deficit, forex reserves, and inflation.
- Government initiatives aim to reduce dependency through electric mobility and biofuels.
- India’s self-sufficiency in crude oil remains low at just 12.3% in FY24.
SC rejects return to ballot paper, poses questions on EVM’s, counting process.
| Syllabus: GS-II; Subject: Polity Topic: Elections and RPA, Issue: Ballot Paper vs EVM’s. |
Context: Supreme Court hearing petitions on Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs).
Concerns Raised by the Supreme Court and Petitioners:
- Doubts about the trustworthiness of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs).
- Lack of complete verification of EVM votes with Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) slips.
- Reluctance of the Election Commission to share EVM source code.
- Potential manipulation of EVMs due to programmable chips.
- Need for transparency in the electoral process to ensure public confidence.
Prelims Connect (Terminology in news)
EVMs:
VVPATs:
|
IMF raises India’s FY25 growth projection to 6.8%.
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Current affairs, Topic: Indices and reports, Issue: Growth Projections. |
Context: World Economic Outlook report released by International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Growth drivers:
- Domestic demand and a growing working-age population.
- Consumer price inflation forecasted to decline gradually.
Challenges: Rising crude oil prices and global supply chain issues.Top of Form
Prelims Connect (Institutions in news):
| International Monetary Funds:
· Promotes global economic growth, financial stability, and poverty reduction. · It provides policy advice, financial assistance, technical assistance, and training to member countries. · Key reports include the World Economic Outlook (WEO), Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR), Fiscal Monitor, and Regional Economic Outlook. |
Centre notifies panel led by Cabinet Secretary on issues of queer community.
| Syllabus: GS-II; Subject: Polity Topic: Rights issues, Issue: Rights of queer community. |
Context: A Cabinet Secretary-led committee formed by the Centre to tackle queer community issues.
Synopsis:
- The six-member committee includes secretaries from key ministries: Home Affairs, Women and Child Development, Health and Family Welfare, Social Justice and Empowerment, and the Law Ministry.
- In Supriyo Chakraborty v Union of India 2024, the Supreme Court declined to recognize same-sex marriage as a fundamental right.
- The committee will outline rights for queer couples, including ration card benefits, joint bank accounts, medical next of kin status, and more.Top of Form
+1 advantage for mains (case law)
Navtej Singh Johar judgement 2018
|
Daily Editorials
Indian origin Gopi Torakura heads to space: what is space tourism?
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Science & Technology, Topic: Space technology, Issue: Space tourism |
Context: Entrepreneur and pilot Gopi Thotakura is set to become the first Indian to venture into space as a tourist on the NS-25 mission of Blue Origin
Space tourism:
- Space tourism offers recreational or business space travel opportunities.
- Includes sub-orbital and orbital missions, with
- Sub-orbital flights reach just beyond the Kármán line.
- The Kármán line is a demarcation between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space. It is set at an altitude of 100 kilometres above mean sea level.
- Orbital spacecraft take passengers much further, allowing for longer stays in space.
Concerns:
- Cost- current prices often exceeding a million dollars per passenger.
- Environmental concerns due to rocket emissions, affecting the upper atmosphere.
- Safety remains a significant issue, with a notable fatality rate among astronauts.
Source: Indian Express
Moving past bonds
| Syllabus: GS-I, Subject: Polity, Topic: Elections and RPA, Issue: Election reforms |
Context: Electoral finance reforms that are needed after Electoral Bonds declared unconstitutional.
Electoral reforms to address concerns of electoral finance:
- Impose expenditure limits on political parties and mandate independent audits.
- Establish a tax-free National Election Fund for donations.
- Ensure internal democracy, transparency, and RTI coverage for political parties.
- Grant legal authority to the ECI to cancel elections for financial misconduct.
- Disqualify individuals with pending heinous offence cases from contesting elections.
- Empower the ECI to de-register political parties that have not contested an election for 10 years, but have benefited from tax exemptions.
- Make paid news an electoral offence with two years’ imprisonment, by declaring it a “corrupt practice” and “undue influence”
| +1 advantage for mains (Statement)
“We should fight against corruption with our full strength. And this is my personal conviction.”(PM Modi) |
Source: Indian Express
Imported inflation
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Inflation, Issue: Imported inflation |
Context: Asian Development Bank warned that India could face imported inflation as the rupee could depreciate amid the rise in interest rates in the West.
Imported Inflation:
- Occurs when the prices of goods and services in a country rise due to increased costs of imports.
Factors responsible for imported inflation:
- Currency depreciation as it makes imports more expensive.
- Higher import costs, such as rising crude oil prices.
Other issues
- Critics argue that costs do not directly determine prices; instead, it is the prices consumers are willing to pay that influence costs.
- Value is imputed from final consumer goods to inputs, shaping the pricing dynamics.
- Even currency depreciation reflects changes in nominal demand rather than directly causing input costs to rise.
Source: The Hindu
Why has India allowed FIIs to invest in its green bonds?
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Global Agreements and Efforts, Issue: Green finance |
Context: RBI has allowed Foreign Institutional Investor (FII) to invest in Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs)
Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs):
- Government debt aimed at funding India’s transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Offer lower interest rates compared to conventional G-Secs, known as a greenium.
- Adoption of greenium is encouraged by financial institutions to accelerate the transition to a greener future.
Measures to facilitate SGrBs
- The 2022-23 Union Budget introduced SGrBs to finance projects such as offshore wind, solar power, and EV transition.
- Concerns about greenwashing led to the release of India’s first SGrB Framework by the Finance Ministry in November 2022.
- The framework lists eligible projects like renewable energy investments, energy-efficient buildings, public transport, and EV subsidies.
Benefits
- Supports funding for ambitious net-zero goals pledged by Prime Minister.
- Diversify green investments and gain green credentials.
- Addresses greenwashing concerns, makes green investments in India attractive.
Source: The Hindu
Reforms needed in the voting process
| Syllabus: GS II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Elections and RPA, Issue: Election reforms |
Context: The Supreme Court hearing petitions seeking 100% cross-verification of the Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) slips with the vote count.
Benefits of Electronic voting machine (EVM):
- Reduced booth capturing by limiting vote casting to four votes per minute.
- Eliminated invalid votes, making the counting process more efficient.
- Eco-friendly, reducing paper consumption in large-scale elections.
- Provide administrative convenience and faster, error-free counting.
- Mechanisms like random allocation and mock polls uphold integrity of the process.
- EVMs are standalone devices, not susceptible to external hacks.
Concerns:
- Doubts persist about EVMs’ susceptibility to hacking among political parties and activists.
- The current sample size for matching EVM count with VVPAT slips may not be scientifically robust, potentially failing to detect defective EVMs.
- Booth-wise polling behavior identification raises concerns about profiling and intimidation.
Measuresto enhance transparency and confidence in the election process:
- 100% use of VVPAT ensures voters can verify their votes.
- A scientific method for deciding the sample size for matching EVM count with VVPAT slips.
- If errors occur, VVPAT slips for the entire region should be counted for accuracy.
- “Totaliser” machines can aggregate votes from multiple EVMs for candidate-wise counts.
| +1 Advantage for mains (Best practices)
· Many western democracies, including France, The Netherlands, and the U.S., have discontinued the use of EVMs for elections. · In Germany, the Supreme Court declared the use of EVMs in elections as unconstitutional in 2009. · Brazil is among the countries that continue to use EVMs for their elections. · Among neighboring countries, Pakistan does not use EVMs, while Bangladesh experimented with them in 2018 but reverted to paper ballots for the general elections in 2024. +1 Advantage for mains(Case law) · In Subramanian Swamy versus Election Commission of India (2013), the Supreme Court mandated a paper trail for ensuring free and fair elections. |
Source: The Hindu
Navigating life as a consumer with disability
| Syllabus: GS- I, Subject: Society and Social Justice, Topic: Welfare schemes, mechanisms, laws and institutions related to disabled,
Issue: Consumers with disabilities |
Challenges faced by disabled consumers:
- Inaccessibility of goods and services and customer support options
- Remains invisible to businesses and corporates
Different reforms to address the concerns of disabled:
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act (RPWDA) and the Consumer Protection Act (CPA) empower consumers with disabilities.
- RPWDA mandates universally designed consumer goods and accessible services.
- Complaints under RPWDA go to Disability Commissions, with non-binding directives.
The way ahead:
- CPA lacks specific provisions for consumers with disabilities, unlike RPWDA.
- Aligning CPA with RPWDA is crucial for equal protection and accessibility.
- Businesses should make offerings accessible to tap the market of persons with disabilities.
- Awareness about rights and resources can be raised through initiatives like Jago Grahak Jago Campaign.
- Government could consider bringing comprehensive accessibility guidelines for all goods and services.
| +1 advantage for mains (Data point)
· In India, persons with disabilities account for 5-8% of the population (World Bank, 2009). |
Source: The Hindu
