

Fertility levels drop below one in many Asian nations.
| Syllabus: GS-I, Subject: Geography, Topic: Population and Migration, Issue: Fertility rate |
Context: Falling fertility rates in various countries below the replacement rate of 2.1 children per woman.
Reasons for declining birth rates:
- Significant shift in cultural attitudes towards family size and child-rearing responsibilities.
- Social shifts, like more opportunities for women in education and careers, declining marriage rates, and the high cost of raising children, are driving down birth rates.
- Many women delay marriage and childbirth to pursue personal and professional goals.
- Stricter family planning measures.
Impact:
- Low birth rates contribute to an aging population, creating economic challenges like higher healthcare costs and a shrinking workforce.
- Governments invest in incentivizing childbirth, but the impact remains uncertain.
Prelims Connect:(Terms in news):
| Total Fertility Rate:
● It is a measure used to estimate the average number of children a woman is expected to have in her lifetime based on current age-specific fertility rates. ● Replacement level fertility: This is the rate needed to maintain a stable population size over time, accounting for mortality rates and other factors. ● Typically considered to be around 2.1 children per woman. ● A TFR below 2.1 indicates that the population is not replacing itself, leading to population decline in the long term. Conversely, a TFR above 2.1 suggests population growth. |
India’s East Asia outreach shows its Central to regional stability.
| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India’s relations with other nations, Issue: East Asia. |
Context: India’s recent Southeast Asia tour highlights regional focus during elections.
Synopsis:
- Historical, cultural, and economic ties shape India’s relations with Southeast Asia.
- Despite ties, recent survey shows low perceived Indian influence.
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is India’s fourth-largest trading partner, indicating growing economic engagement.
- Act East policy emphasizes connectivity for economic growth.
- Indo-Pacific policy stresses ASEAN centrality and adherence to international law.
- South China Sea tensions drive India’s maritime security interests.
| Look East Policy:
● Initiated in 1991, the Look East Policy aimed to strengthen ties with Southeast Asia. ● It focused on economic, strategic, and cultural cooperation to counterbalance China’s influence. ● In 2014, it evolved into the Act East Policy, expanding focus to East Asian countries like Japan and South Korea. ● The Act East Policy includes the Pacific region, emphasizing economic, cultural, and strategic ties. ● It ensures continuous engagement at bilateral, regional, and multilateral levels for comprehensive cooperation. |
Government may issue green bonds for up to rupees 25000 crore in FY 25
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Financial markets, Issue: Green Bonds. |
Context: India plans to increase the sale of green bonds to finance sustainable infrastructure projects this fiscal year.
Synopsis:
- Demand for sustainable bonds is high in the market, leading to increased borrowing through green bond instruments.
- Including Indian government bonds in international indices has attracted foreign portfolio investors, boosting interest in Indian government securities.
Prelims Connect (Terminology in news):
| Green Bonds:
● Green bonds fund eco-friendly projects like renewable energy. ● Introduced by development banks in 2007, expanded to include corporates in 2013. ● The Securities and Exchange Board of India regulates issuance for transparency. ● Benefits include enhanced issuer reputation and cost-effective capital. ● Crucial for financing sunrise sectors like renewable energy, promoting sustainable growth. |
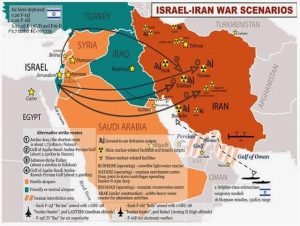
India seriously concerned over Iran Israel hostilities.
| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Global issues, Issue: Iran-Israel attack. |
Context: India expresses concern over Iran-Israel tensions, and calls for de-escalation.
Concerns:
- Direct attack by Iran on Israel raises concerns, indicating intent.
- Potential escalation threatens regional stability and impacts energy prices.
- India maintains strategic relationships with both countries, influencing its foreign policy.

Daily Editorials
India’s hepatitis headache
| Syllabus: GS-I, Subject: Society and social justice, Topic: Social Sector- Health, Issue: World Health Organization’s (WHO’s) Global Hepatitis Report 202 |
Hepatitis:
- Viral hepatitis includes hepatitis A, E, B, C, and D, with B and C posing significant health risks.
- Hepatitis B can be prevented by vaccination, while hepatitis C can be cured with medication.
- Hepatitis D can only infect those who are already infected with hep B.
- In India, hep B transmission is largely through mother-to-child transmission, while hep C infections are common among injection drug users.
- Challenges in controlling hepatitis B include ensuring full vaccination coverage and providing timely treatment.
- Treatment coverage for hepatitis B and C in India is notably lower than for tuberculosis, despite comparable mortality rates and cheaper availability.
- Improving vaccination coverage and treatment access are crucial for addressing viral hepatitis in India.
| +1 advantage for mains:
Key findings of the WHO’s Global Hepatitis Report 2024: ● India has one of the highest burdens(11% of the global burden) of viral hepatitis globally, ranking second only to China. ● India is among 10 countries where 80% of hepatitis C infections are among injection drug users. Key facts related to hepatitis in India: ● The hepatitis B vaccine was introduced in India’s universal immunization program in 2007-08. ● The National Viral Hepatitis Control Programme in 2018 included provisions for vaccinating high-risk groups like healthcare workers against hepatitis B. |
Source: Indian Express
Food for reform
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Agriculture and allied, Issue: Reforms in Agri-food space |
Reforms needed in Agri-food space:
- Focus on food systems transformation for sustainable agriculture.
- Invest in Agri-R&D, innovations, and extension for increased productivity.
- Address climate change impacts with climate-resilient agriculture and water management.
- Prepare for urbanization with improved logistics and value chains for food distribution.
- Promote Farmer Producer Organizations to empower smallholders and create scale.
- Shift from food security to nutritional security through fortification of staples.
- Encourage PPP for efficient value chains and climate-resilient seeds.
- Repurpose subsidies towards direct income transfers for farmers’ welfare and agricultural development.
| +1 advantage for mains( Datapoint): Last year’s El Nino effect led to agri-GDP growth dropping from 4.7 per cent in 2022-23 to just 0.7 per cent in 2023-24 (as per the second advance estimate). |
Source: Indian Express
The Asian edge
| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests, Issue: Block politics in Asia |
Context: US President’s summits with the leaders of Japan and the Philippines
Key takeaway from the summit:
- Summit signal Japan’s shift from a passive to a potential military powerhouse in Asia.
- Japan agreed to integrate military command structures with the US and boost defense capabilities.
- Japan aims to deter Chinese military coercion and uphold a rules-based Indo-Pacific.
- Japan pledged to defend the Philippines’ territorial sovereignty in South China Sea.
- Kishida and Biden discussed economic cooperation with Manila as an alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
China’s reaction to the summit
- China warns against “bloc politics” and the formation of a “mini NATO” in Asia.
- China hosted Russian and Taiwanese leaders and leaders from Vietnam and Indonesia, to bolster regional ties.
- China seeks to prevent economic decoupling from China and the formation of a US-backed coalition among its neighbors.
The way ahead for India:
- US-China confrontation in Asia has global implications.
- India’s partnership with the US and border standoff with China give it a key role in Asian affairs.
- Speculation arises in Delhi about Chinese efforts to prevent India-US alignment.
- Past letdowns urge caution regarding Chinese outreach.
- Restoring peace on the India-China border is crucial before considering a political reset.
Source: Indian Express
What is doxing? What measure you take if it happens to you?
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Science & Technology, Topic: Computer and ICT, Issue: Cyber technology – basics, attacks and solutions |
Doxxing:
- It involves publicizing private details like addresses, phone numbers, and medical information, obtained illegally.
- Even sharing semi-public content without consent can lead to doxxing and harassment.
Concerns:
- Intent behind sharing matters; malicious intent can lead to platform action.
- Victims face physical, digital, and emotional threats, affecting security and daily life.
Options that the victims have:
- Keep an incident log, report to platforms, change passwords, and file reports.
- Report through the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal and file an FIR.
The way ahead:
- Platforms like Meta and Google offer tools and policies to address doxxing.
- Social media companies must adhere to India’s IT Rules.
- Victims can return to social media after ensuring security but should have a self-care plan and support network.
Source: The Hindu
Decoding the judgment on Jim Corbett
| Syllabus: GS III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Biodiversity and Conservation, Issue: Biodiversity Conservation |
Context: The Supreme Court exposed a corrupt network involving politicians, forest officials, and contractors responsible for cutting down 6,000 trees in Jim Corbett.
Key points in Supreme Court ruiling
- Emphasized an eco-centric approach over anthropocentrism in ecotourism.
- Banned tiger safaris in core areas and formed a committee to assess their feasibility in peripheral zones across India.
- Rejected the 2019 NTCA guidelines allowing zoo-like safaris in national parks.
- Insisted that tigers for safaris must be sourced from the same landscape,
- Ruling invoked the precautionary principle to minimize environmental damage, citing the threat of mass extinction.
- The precautionary principle applies beyond tigers to all endangered species.
Concerns remaining:
- The Supreme Court’s plan to recover restoration costs lacks a clear methodology.
- Recovering costs does not necessarily restore the environment’s ability to provide goods and services.
| +1 Advantage for mains
Different principle to access the damage to the ecosystem ● The European Liability Directive defines conservation status as influences affecting habitat and species long-term survival. ● India’s valuation framework pre-T.N. Godavarman case aimed to replace lost forests with compensatory plantations. ● Compensatory afforestation levy and net present value (NPV) are India’s current valuation choices. ● The International Court of Justice in Costa Rica v. Nicaragua (2018) asserts damage to the environment and loss of its ability to provide goods and services are compensable. |
Source: The Hindu
Urbanization, no liberating force for Dalit
| Syllabus: GS- I, Subject: Society and Social justice, Topic: Salient features of Indian Society, Issue: Caste system in urban area |
Caste based discrimination in urban area:
- Caste often overrides skill, hindering equal opportunities in the economy.
- Dalit and Muslim neighborhoods face inadequate public services.
- Dalit and Muslims disproportionately live in polluted areas like landfills.
- Forced evictions disproportionately affect Dalit and Muslim communities.
| +1 advantage for mains(Report)
● A recent report by the Housing and Land Rights Network on forced evictions in India also shows that Dalits and Muslims are the most impacted by slum demolition drives. Ambedkar and Phule on urbanization and caste ● Ambedkar rejected village life, seeing it as a stronghold of caste domination. ● He viewed urbanization as a path to Dalit liberation, weakening caste oppression. ● Cities offered anonymity, enabling transition from caste-based to class-based identities. ● Jyotirao Phule also favored city life for its liberal opportunities and economic freedom. Gandhi on Indian villages ● He saw the Indian village as a self-reliant, equitable and a just non-violent order, ● Argued for the decentralization of power to the villages through Gram Swaraj. |
Source: The Hindu
