ED can summon anyone for any information: SC.
| Syllabus: GS-II; Subject: Current affairs Topic: Important supreme court judgements, Issue: ED Summons. |
Context: The Supreme Court upheld the Enforcement Directorate’s (ED) powers to summon individuals for information.
Gist:
- Criticised Tamil Nadu District collectors for not responding to ED summons, and accused them of disrespecting law, court, and Constitution.
- Endorsed the sweeping powers of ED to summon anyone for any information.
Prelims Connect (Institutions in news)
| Enforcement Directorate:
● Under the administrative control of the Department of Revenue (Ministry of Finance). ● Functions include enforcing the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA), the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) and the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA). ● Empowered to attach assets of offenders and undertake actions like search, seizure, arrest, and prosecution under PMLA. |
India risking demographic dividend.
| Syllabus: GS-I, Subject: Geography, Topic: Population and Migration, Issue: Demographic Dividend. |
Context: World Bank warns South Asia, including India, failing to utilize demographic dividend.
Prime concerns:
- Job creation lags behind working-age population growth.
- India’s employment growth below average for 2000-2023, with the employment ratio declining second only to Nepal.
- Region could achieve 16% higher output growth with better employment rates.
- Weak employment trends in non-agricultural sectors due to institutional and economic challenges.
Recommendations include supporting women’s participation, increasing access to finance, trade openness, easing financial regulations, and improving education.
| Demographic dividend:
● Economic growth potential from age structure changes. ● Arises when the working-age population (15-64) exceeds dependents. ● Leads to increased productivity, savings, and investment. ● Requires employment opportunities, education, and skill development for full realization. |
India’s new EV policy allows imports from any country, including China: Official.
| Syllabus: GS-III; Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management; Topic: Indian Initiatives, efforts and Commitments, Issue: EV Policy. |
Context: India’s new EV policy allows imports of electric vehicles from any country, including China.
Policy Includes:
- Lowering import taxes on certain electric vehicles.
- Car manufacturers must commit to investing at least $500 million and commence domestic manufacturing within three years to benefit from the tax reduction.
- Aim: To encourage investment and production of electric vehicles within India.
- Impact: It could potentially increase the availability of electric vehicles in the Indian market, including those from Chinese manufacturers.
Prelims Connect (Policies/Schemes/Programs)
| New Electric Vehicle Policy 2024:
✔ Customs duty cut to 15%. ✔ Minimum Investment required: Rs 4150 Cr ✔ No limit on maximum Investment ✔ Timeline for manufacturing: 3 years for setting up manufacturing facilities in India, and to start commercial production of e- vehicles, and reach 50% domestic value addition (DVA) within 5 years at the maximum. ✔ Domestic value addition (DVA) during manufacturing: A localization level of 25% by the 3rd year and 50% by the 5th year will have to be achieved Key Benefits: ✔ Drives innovation and local manufacturing. ✔ Reduces oil imports, pollution. ✔ Aligns with emission reduction goals. |
Daily Editorials
What is Kallakkadal, which has flooded houses in Kerala’s coastal areas?
| Syllabus: GS-I, Subject: Geography, Topic: Climatology, Issue: Kallakkadal |
Context: Hundreds of houses have been flooded in coastal areas of Kerala due to high swell surge or Kallakkadal.
Kallakkadal
- A combination of two Malayalam words meaning “thief” and “sea,” symbolising the ocean’s sudden arrival.
- Refers to coastal flooding caused by swell waves during the pre-monsoon season on the southwest coast of India.
Factors responsible for formation:
- Caused by ocean swells generated by distant storms or intense gale winds, travelling thousands of kilometres until they reach the shore.
- Strong winds in the southern Indian Ocean generate ocean swells, which then move northward to affect the Kerala coast and Lakshadweep.
Concerns
- Kallakkadal occurs without precursors or local wind activity (challenging to predict)
Preparedness measure: Early warning systems like the Swell Surge Forecast System offer forecasts up to seven days in advance.
Source: Indian Express
Atmanirbhar in defense
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Internal Security, Topic: Emerging Security challenges, Issue: Defense indigenization |
Transformation in India’s defence ecosystem:
- Defence ecosystem in India has seen significant transformations with a focus on indigenization, domestic procurement, and defence
- India aims to achieve a defence production target of Rs 1,35,000 crore in 2023-24 and Rs 1,75,000 crore by 2025.
Steps for defense indigenization:
- Policies like Atmanirbhar Bharat and Make In India aim to reduce risks associated with disruptions in critical supply chains.
- Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020 mandates 50% indigenous content in procurement contracts and introduces the Buy (Global-Manufacture in India) category.
- Initiatives like Srijan Indigenisation Portal and defence industrial corridors in Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh have attracted significant investments.
- Progress in building naval platforms like INS Vikrant aircraft carrier and Project 17A frigates, demonstrates advancements in indigenous defence capabilities.
- Initiatives like Innovations for Defence Excellence and funding schemes support innovation and participation of MSMEs, startups, and academia in defence R&D.
The way ahead:
- Provide equal career opportunities for women in the armed forces.
- The transformation in the defence sector aligns with the goal of making India a resilient and self-reliant nation by 2047, fostering global partnerships in defence.
| +1 advantage for mains ( Data points)
● Capital acquisition budget for domestic procurement increased from 40% in 2020-21 to 75% in 2023-24. ● India ranked among the top 25 arms exporters by SIPRI for the first time in 2019, securing the 23rd position. ● India set a defence exports target of Rs 35,000 crore by 2025. |
Source: Indian Express
How Delhi maps the world
| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India’s foreign policy, Issue: Evolution of India’s foreign policy |
India’s foreign policy:
- India’s strategic geography has expanded to include island states and territories from the South Pacific to the African coast.
- The concept of the “Indo-Pacific” has gained prominence, driven by India’s evolving relations with China and the US.
- India’s engagement with Europe has increased, marked by high-level visits, growing trade, and agreements with the European Free Trade Association.
- The expansion of India’s geographic vocabulary has led to increased focus on regions like Europe, the Middle East, and Africa.
- Amid this expansion, “South Asia” has seen a decline, with SAARC’s failure prompting a shift towards sub-regional cooperation.
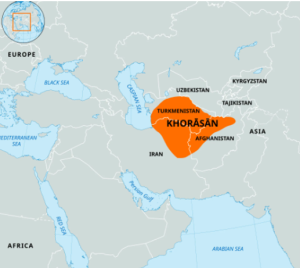
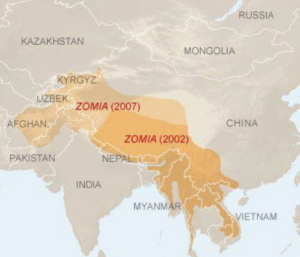
- New geographies like “Zomia” and “Khorasan” are gaining strategic attention due to emerging challenges and tensions in regions surrounding India.
| Prelims Connect (Places in news):
● Khorasan in Persian means the land of the rising sun. It refers to Persia’s eastern borderlands, including parts of modern Pakistan, Afghanistan and Central Asia.
● Zomia– an academic term for a region where the highlands of North East India, South West China, and SouthEast Asia meet. ● It’s a region where centralized state control has been traditionally weak and is full of minority populations, some of whom straddle across formal state borders.
|
Source: Indian Express
Will india experience more heatwave days this summer
| Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management, Topic: Disasters, Issue: Heatwaves |
Context: The IMD forecasts above-normal temperatures across most of India from April to June.
Heat waves:
- A period of unusually high temperatures, with specific thresholds defined by the IMD.
- IMD declares a heat wave if maximum temperatures reach at least 40°C in the plains or 30°C in hilly regions, with departures of 4.5-6.4°C from normal.
- A heat wave is also declared if actual maximum temperatures exceed 45°C, with severe heat waves above 47°C.
Factors responsible for heatwaves:
- Climate change contributes to more frequent and lethal heat waves globally.
- El Niño weather conditions are also influencing heat wave occurrences.
Concerns:
- Significant risks to public health, agriculture, livelihoods, and disease spread.
- Higher temperatures can cause heat stress, illness, and mortality
The way ahead:
- The Election Commission of India has issued an advisory to manage the impact of heat waves during voting,
Source: The Hindu
Is the Katchatheevu island disputed.
| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India and its neighborhood, Issue: India-Sri Lanka relations |
Context: Katchatheevu Island issue
Katchatheevu Island:
- Katchatheevu became part of Sri Lanka through an agreement signed in 1974.
- The islet is historically significant for fisher folk from both India and Sri Lanka, hosting an annual festival at St. Anthony’s Church.
- The 1974 agreement faced opposition in the Indian Parliament, leading to debates and walkouts, particularly from Tamil Nadu politicians.
- The issue resurfaced in 1991, with Tamil Nadu Chief Minister demanding retrieval.
- The Union government’s stance, as of 2013 and 2022, asserts that Katchatheevu is under Sri Lankan jurisdiction, with no territory ceded by India.
Source: The Hindu
Poll campaigns in India must reflect climate issues
| Syllabus: GS II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Elections and RPA, Issue: Climate change issue in elections. |
Findings of World Meteorological Organization (WMO)’s State of the Global Climate report-2023
- 2023 is the hottest year globally.
- Average temperature rise from pre-industrial levels is 1.45°C, nearing the 1.5°C limit.
- Record-breaking events – ocean temperature rise, glacier retreat Sea levels are rising
- These events disrupt activities, including agriculture, affecting development globally.
Steps to address climate change:
- The Paris Agreement became legally binding in 2016.
- India has implemented initiatives such as the National Action Plan on Climate Change and the National Solar Mission to shift towards renewable energy.
The way ahead:
- The timing of the State of the Global Climate report is opportune for political discourse.
- Political parties should address climate change concerns and outline action plans.
Source: The Hindu
A new low: On Israel’s Gaza war and the U.S. response
| Syllabus: GS- II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Global Issues, Issue: USA’s response to the Israel’s Gaza war |
Context: UNSC resolution for ceasefire in Gaza adopted.
USA’s response to the Israel’s Gaza war:
- Historically, the U.S. has supported Israel’s military actions in Palestine.
- It took five and a half months for the USA to allow a UNSC resolution for a ceasefire.
- Despite the resolution, the USA is not enforcing it, tarnishing its global image.
- The USA continues to support Israel despite criticism, unlike past presidents who applied pressure.
Conclusion:
- The US administration must demand an immediate ceasefire, boost aid to Gaza, and stop arms sales to Israel if the conflict continues.
Source: The Hindu