Joint fund to support Indo-Pac start-ups
Syllabus: GS-II Subject: International Relations Topic: Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests, Issue: Indo Pacific
Context: India and France plan to launch a fund to support startups and climate-focused innovations in the Indo-Pacific region.
Synopsis:
- Projects likely to be funded in the Western Indian Ocean and broader Indo-Pacific.
- This initiative stems from the Indo-Pacific Triangular Cooperation (IPTDC)
| The Indo-Pacific Triangular Cooperation Fund (IPTDC) ;:
✔ Collaboration between India and France to support climate and SDG-focused innovations and start-ups in the Indo-Pacific. ✔ Aim to scale up green technologies in the region through Triangular Development Cooperation(India, France and third country in the Indo Pacific). ✔ Provides transparent funding alternatives to innovators and is a key aspect of the India-EU Connectivity Partnership. |
Source: Mint
IL&FS’s new board moves NCLAT urges it to curb PSB from tagging group firms as wilful defaulters.
Syllabus: GS-III Subject: Economy(E) Topic: Banking and Financial Intermediaries, Issue: NCLAT.
Context: IL&FS’s new board seeks NCLAT intervention to prevent 11 public sector banks from declaring group firms as “wilful defaulters.”
Key Issues:
- IL&FS alleges banks of violating orders, and harassing directors;
- Urges NCLAT to restrain coercive actions, and safeguard interests during resolution.
Prelims Connect (Institutions in news)
| NCLAT(National Company Law Appellate Tribunal) :
● Established in 2016 under the Companies Act, ● Functions: Reviewing appeals on ● NCLT decisions under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), ● Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India decisions ● Competition Commission of India (CCI). ● It ensures timely disposal of appeals, typically within six months. |
Source: The Hindu
Vaccine for dengue may be available commercially by mid-2026
Syllabus: GS-III ; Subject: Science & Technology (T); Topic:Medical science and Health, Issue: Vaccine for Dengue.
Context: Indian Immunological Limited, a subsidiary of the National Dairy Development Board, is making significant strides in vaccine development
Vaccine Development:
- Vaccine potentially available commercially by mid-2026.
- Also developing vaccines for the Zika virus and Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD).
- Launched Hepatitis A vaccine, Havisure recently.
Prelims Connect
| 1. Zika Virus:
● Transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. ● Can cause birth defects. ● No specific treatment or vaccine is available. 2. Dengue: ● Spread by Aedes mosquitoes. ● Symptoms include fever, severe headache, and joint pain. ● Severe cases can be life-threatening. 3. Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD): ● Transmitted by ticks. ● Symptoms include fever, headache, and muscle pain. ● Endemic in forested regions of India, particularly Karnataka. |
Source: The Hindu
Centre notifies rules allowing transfer of ‘captive’ elephants
Syllabus: GS-III; Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management Topic: Indian Initiatives, efforts and Commitments, Issue: Captive Elephants rules.
Context: The government has issued new rules, called the Captive Elephant (Transfer or Transport) Rules, 2024.
Key points:
- Elephants can be transferred when the owner can’t maintain them or for better upkeep, approved by the Chief Wildlife Warden.
- Genetic profiling registration is necessary before transferring elephants between states.
- Amendments to the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 allow transfer only for elephants with existing ownership certificates.
- Controversy: Recommendations to limit transfers were made but not implemented, retaining the allowance for captive elephant movement.
Prelims Connect (Policies/Schemes)
| Project Elephant (1992):To safeguard elephants, mitigate human-elephant conflicts, and ensure their welfare.
✔ Through 31 elephant reserves, including recent additions like Dandeli in Karnataka and Singphan in Nagaland. ✔ Leading states: Karnataka > Assam >Kerala. ✔ Asian elephants o IUCN status: Endangered o Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I o CITES: Appendix I |
Source: The Hindu
Study reports evidence of ‘missing’ spring in India
Syllabus: GS-I Subject: Geography Topic: Indian Climate, Issue: Missing Spring Season in India
Context: Climate trends indicated a disappearance of spring, traditionally occurring between winter and summer.
Study Findings:
- February stands out as a month of significant warming across all regions analysed.
- Contrast between January (cooling or slight warming) and February (strong warming) suggests abrupt transitions from cooler to warmer conditions.
Causes:
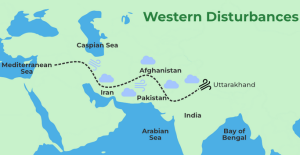
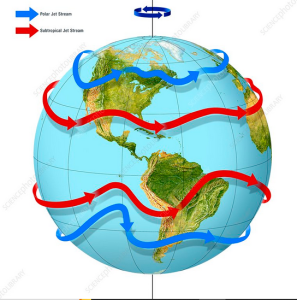
- Alterations in the pattern of Western Disturbances and the jet stream are cited as causes for these changes.
| Western disturbances are extratropical storms that originate in the Mediterranean region and bring rain and snow to the northwestern parts of the Indian subcontinent.
Jet streams are fast-moving, narrow air currents high up in the tropopause, the boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere. Generally blow from west to east (westerly winds).
|
Source: The Hindu
Star-rating for state environment bodies not operational yet, Ministry tells NGT
Syllabus: GS-III; Subject: Environment, Ecology and Disaster Management; Topic: Environmental Impact Assessment, Issue: Star ratings for State environment bodies.
Context: The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change planned star-rating for state environmental efficiency.
About Star Ratings:
- The plan is aimed to rank State Environment Impact Assessment Authorities (SEIAAs) based on efficiency in granting clearances.
- SEIAAs receive points ranging from 0 to 7 based on clearance efficiency, with criteria specified.
- This System was introduced in 2022 but challenged for potentially diluting scrutiny during assessments.
Prelims Connect (Institutions in news)
| State-Level Environment Impact Assessment Authorities:
● Central Government forms SEIAAs under the Environmental Protection Act 1986. ● Functions: To grant Environmental Clearance to mitigate pollution and protect the environment. ● Projects are categorized as ‘A’ or ‘B’ based on their potential environmental impact. ➢ Category ‘A’ projects require clearance from Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEF&CC), GoI. ➢ Category ‘B’ projects require clearance from State Environment Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA), based on activity thresholds. |
Source: Indian Express
Daily Editorials
Heat, aridity, clear skies: why forests are already ablaze in the Nilgiris
Syllabus: GS-I, Subject: Geography, Topic: Geo-physical Phenomenon, Issue: Forest fires
Context: Forest fires in Nilgiris in Tamil Nadu
India’s vulnerability to forest fire:
- November to June is considered the forest fire season in India.
- Over 36% of India’s forest cover is prone to frequent fires.(ISFR-2019)
- Approximately 4% of forest cover is ‘extremely prone’ to fire, while another 6% is ‘very highly’ fire prone.
Factors responsible for forest fire:
- Natural: Hot and dry temperatures, high tree density, and conducive weather conditions.
- Human carelessness such as discarded cigarettes or natural causes like lightning strikes.
This year, high aridity, above-normal day temperatures, clear skies, and calm winds in southern India have led to a spike in forest fire incidents.
Source: Indian Express
Warming up to climate change: Why do global sea surface temperatures matter?
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Ecology and environment, Topic: Global Warming and Climate Change, Issue: Rise in sea surface temperature
Context: February 2024 recorded the highest average global sea surface temperature (SST) since 1979.
Factors responsible for rise in sea surface temperature
Man made:
- Burning fossil fuels have released high levels of greenhouse gases(GHGs) into the atmosphere, trapping heat and causing global warming.
- Nearly 90% of the extra heat trapped by GHGs has been absorbed by the oceans.
Natural:
- El Niño: contributed to ocean warming and rising global surface temperatures.
- Weaker winds over the Sahara Desert have reduced the amount of dust blowing into the Atlantic Ocean, allowing more sunlight to penetrate and heat the ocean.
Concerns:
- Leads to increased ocean stratification, making it harder for water layers to mix, affecting nutrient distribution and oxygen levels.
- Threatens marine life survival by affecting nutrient availability, particularly phytoplankton, which forms the base of marine food webs.
- More frequent and intense marine heatwaves, contributing to coral bleaching, disrupting migration patterns, and affecting aquatic ecosystems.
- More frequent and intense storms– resulting in heavier rainfall, stronger winds, and increased flooding, posing greater risks to coastal communities.
The way ahead:
To mitigate these consequences, reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential.
Source: Indian Express
The MIRV leap that fires up India’s nuclear deterrence
Syllabus: GS-III, Subject: Science and technology, Topic: Defense, Issue: Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicles (MIRVs).
Context: India successfully tested Agni-5 missile with MIRV technology under Mission Divyastra.
Significance:
- Enable simultaneous strikes on multiple targets.
- Places India among a select group of nations (USA, Russia, China, France and UK).
- Restores balance in the Sino-Indian nuclear deterrent
- Demonstrates India’s ability to meet complex technical requirements of MIRV.
Conclusion: India’s upcoming test of a long-range Submarine Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM) will further strengthen India’s nuclear arsenal.
What do FTAs with European countries signal?
Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India’s relations with other nations, Issue: India-EFTA Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA)
Context: India signed a trade and economic partnership with EFTA countries.
Key points of the Act:
- Investment: TEPA aims for $100 billion investment in India, creating one million jobs over 15 years.
- Trade in Goods: Provides tariff concessions for EFTA exports to India, excluding gold, dairy, soya, and sensitive agricultural products.
- Trade in Services: Commits to liberalization across sectors, allowing access for Indian professionals, easing qualification recognition
- Sustainable Development: Focus on environment and labor aspects and sustainable development.
- Intellectual Property Rights:Addresses concerns of EFTA pharmaceutical and technology companies .
Conclusion
Successful conclusion of TEPA signals India’s commitment to trade liberalization amid global protectionism.
Source: The Hindu
All eyes are now on the Indian Ocean region
Syllabus: GS II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India’s Foreign Policy, Issue: Indian Ocean region
Geopolitical situation in Indian Ocean:
- Maldives is strengthening its relationship with China.
- Sri Lanka imposed a yearlong moratorium on foreign research ships, including Chinese vessels, showing sensitivity to India’s security concerns.
- India and Mauritius inaugurated a new airstrip and jetty in the Agaléga Islands under India’s SAGAR policy.
Recent developments in Indian Ocean:
- Diversion of Merchant shipping traffic to Indian Ocean amid Israel-Houthi conflict.
- China’s quest for naval bases, with existing presence in Djibouti, Kyaukphyu, Gwadar, and Hambantota.
- Ambiguity in European nations’ stand toward China’s aggressive actions due to geographical distance.
- Underperformance of Indian Ocean Rim Association and risk of losing a key member(Maldives) in Colombo Security Conclave.
The way ahead:
- Prioritize the Indian Ocean region within Indo-Pacific responsibilities.
- Encouraging the formation of a new mechanism like the Indian Ocean Cooperation Organization to enhance maritime security and boost the Blue Economy.
- Increase budgetary allocations to bolster the Navy capabilities
Source: The Hindu
Violence, homelessness, and women’s mental health
Syllabus: GS- I, Subject: Society and Social Justice, Topic: Issues of women, Issue: Mental health issues in women
Mental health issues in women:
- NHFS-5 reveals 30% of women aged 18-49 in India experience physical violence since age 15, with 6% reporting sexual violence.
- Evidence suggests a reciprocal relationship between violence and mental health conditions.
- Structural barriers like poverty and caste, along with violence, lead to a loss of agency and disrupt conventional notions of home.
Concerns:
- Mainstream discussions are limited to depression and anxiety, sidelining the link between violence and psychological distress.
The way ahead:
- Solutions to violence against women should tackle systemic issues like
- unpaid labor,
- economic empowerment, and
- gender norm challenges through education.
Exploring intersectionality and power dynamics, using feminist standpoint theory, can enrich the comprehension of mental health.
Source: The Hindu